Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Without drawing the triangles write all six pairs of equal measures in the following pairs of congruent triangles.
∆STU ≅ ∆DEF
उत्तर
We know that, corresponding parts of congruent triangles are equal.
∠S = ∠D, ∠T = ∠E and ∠U = ∠F
ST = DE, TU = EF and SU = DF
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If ΔABC ≅ ΔABC is isosceles with
In an isosceles triangle, if the vertex angle is twice the sum of the base angles, then the measure of vertex angle of the triangle is
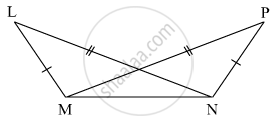
As shown in the following figure, in ΔLMN and ΔPNM, LM = PN, LN = PM. Write the test which assures the congruence of the two triangles. Write their remaining congruent parts.
In the pair of triangles given below, the parts shown by identical marks are congruent. State the test and the one-to-one correspondence of vertices by which the triangles in the pair are congruent, the remaining congruent parts.
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:

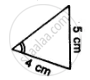
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(∠B = 70°,BC = 6cm,∠C = 50°);
ΔXYZ;(∠Z = 60°,XY = 6cm,∠X = 70°).
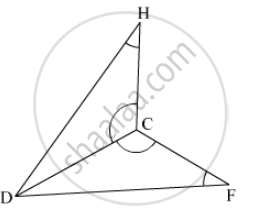
In the figure, BC = CE and ∠1 = ∠2. Prove that ΔGCB ≅ ΔDCE.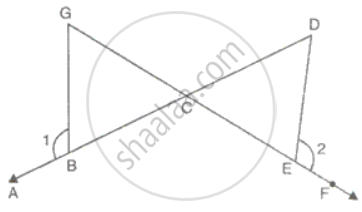
Given that ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF List all the corresponding congruent angles
If AB = QR, BC = PR and CA = PQ, then ______.
“If two sides and an angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and an angle of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent.” Is the statement true? Why?
