Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
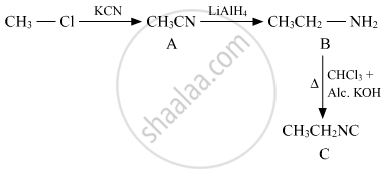
Write the structures of A, B and C in the following:

उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
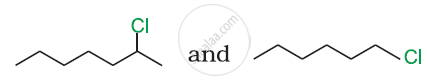
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
Given reasons: SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
Optically active isomers but not mirror images are called ____________.
SN2 mechanism proceeds through intervention of ____________.
An organic molecule necessarily shows optical activity if it ____________.
Among the following, the dissociation constant is highest for:
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
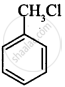
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
Which of the following is the definition of chirality?
Which one of the following compounds is more reactive towards SN1 reaction?
