Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
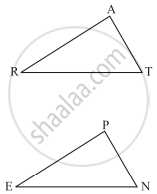
You want to show that ΔART ≅ ΔPEN,
If it is given that ∠T = ∠N and you are to use SAS criterion, you need to have
1) RT = and
2) PN =
उत्तर
1) RT = EN
2) PN = AT
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
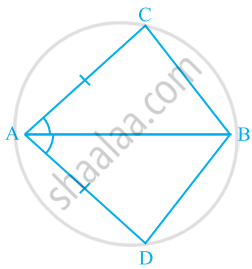
In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisects ∠A (See the given figure). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔABD. What can you say about BC and BD?
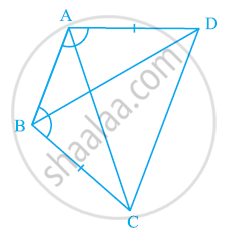
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA (See the given figure). Prove that
- ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
- BD = AC
- ∠ABD = ∠BAC.
In the given figure, AC = AE, AB = AD and ∠BAD = ∠EAC. Show that BC = DE.
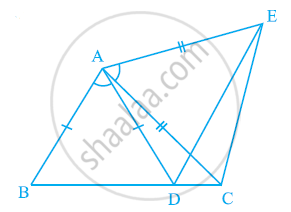
Prove that the perimeter of a triangle is greater than the sum of its altitudes.
In two congruent triangles ABC and DEF, if AB = DE and BC = EF. Name the pairs of equal angles.
ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. BE and CF are its two medians. Show that BE = CF.
The following figure shows a circle with center O.
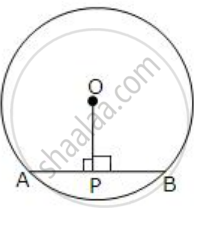
If OP is perpendicular to AB, prove that AP = BP.
In a triangle ABC, D is mid-point of BC; AD is produced up to E so that DE = AD.
Prove that :
(i) ΔABD and ΔECD are congruent.
(ii) AB = CE.
(iii) AB is parallel to EC
From the given diagram, in which ABCD is a parallelogram, ABL is a line segment and E is mid-point of BC.
Prove that: AB = BL.
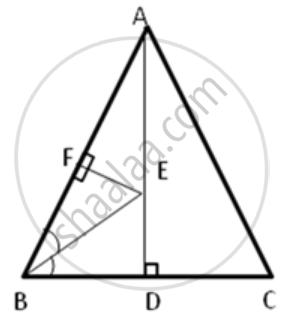
In the following figure, AB = AC and AD is perpendicular to BC. BE bisects angle B and EF is perpendicular to AB.
Prove that: BD = CD