Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following figure, AB = AC and AD is perpendicular to BC. BE bisects angle B and EF is perpendicular to AB.
Prove that: BD = CD
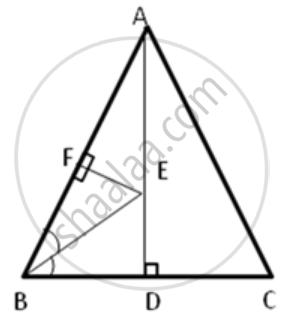
उत्तर
In ΔADB and ΔADC,
∠ADB = ∠ADC ...(Since AD is perpendicular to BC)
AB = AC ...(given)
AD = AD ...(common side)
∴ ΔADB ≅ ΔADC ...(RHS congruence criterion)
⇒ BD = CD ...(cpct)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
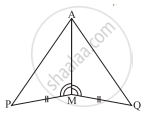
You have to show that ΔAMP ≅ AMQ.
In the following proof, supply the missing reasons.
| Steps | Reasons | ||
| 1 | PM = QM | 1 | ... |
| 2 | ∠PMA = ∠QMA | 2 | ... |
| 3 | AM = AM | 3 | ... |
| 4 | ΔAMP ≅ ΔAMQ | 4 | ... |
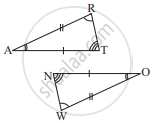
In the figure, the two triangles are congruent.
The corresponding parts are marked. We can write ΔRAT ≅ ?
In Δ ABC, ∠B = 35°, ∠C = 65° and the bisector of ∠BAC meets BC in P. Arrange AP, BP and CP in descending order.
In the given figure, prove that:
CD + DA + AB + BC > 2AC
If the following pair of the triangle is congruent? state the condition of congruency:
In ΔABC and ΔQRP, AB = QR, ∠B = ∠R and ∠C = P.
The given figure shows a circle with center O. P is mid-point of chord AB.
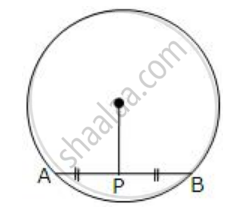
Show that OP is perpendicular to AB.
From the given diagram, in which ABCD is a parallelogram, ABL is a line segment and E is mid-point of BC.
Prove that: AB = BL.
In the given figure: AB//FD, AC//GE and BD = CE;
prove that:
- BG = DF
- CF = EG
In the following figure, AB = AC and AD is perpendicular to BC. BE bisects angle B and EF is perpendicular to AB.
Prove that : ED = EF

In the following figure, OA = OC and AB = BC.
Prove that: ΔAOD≅ ΔCOD
