Advertisements
Advertisements
Solve for x:
5tan–1x + 3cot–1x = 2π
Concept: Inverse Trigonometric Functions
If `tan^-1 ((x - 1)/(x + 1)) + tan^-1 ((2x - 1)/(2x + 1)) = tan^-1 (23/36)` = then prove that 24x2 – 23x – 12 = 0
Concept: Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Let L be a set of all straight lines in a plane. The relation R on L defined as 'perpendicular to' is ______.
Concept: Types of Relations
Let A be a non-empty set.
Statement 1: Identity relation on A is Reflexive.
Statement 2: Every Reflexive relation on A is an Identity relation.
Concept: Concept of Relation > Types of Relations - Identity Relation
The value of cosec `[sin^-1((-1)/2)] - sec[cos^-1((-1)/2)]` is equal to ______.
Concept: Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
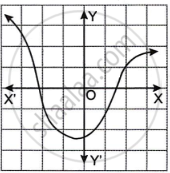 |
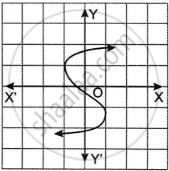 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
Concept: Types of Functions
Let `f : R {(-1)/3} → R - {0}` be defined as `f(x) = 5/(3x + 1)` is invertible. Find f–1(x).
Concept: Composition of Functions and Invertible Function
If f : R `rightarrow` R is defined by `f(x) = (2x - 7)/4`, show that f(x) is one-one and onto.
Concept: Types of Functions
Solve for x: `sin^-1(x/2) + cos^-1x = π/6`
Concept: Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
If sin–1x + sin–1y + sin–1z = π, show that `x^2 - y^2 - z^2 + 2yzsqrt(1 - x^2) = 0`
Concept: Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Statement 1: The intersection of two equivalence relations is always an equivalence relation.
Statement 2: The Union of two equivalence relations is always an equivalence relation.
Which one of the following is correct?
Concept: Types of Relations
If a relation R on the set {a, b, c} defined by R = {(b, b)}, then classify the relation.
Concept: Types of Relations
Find the value of `tan^-1(x/y) + tan^-1((y - x)/(y + x))`
Concept: Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Solve:
sin–1(x) + sin–1(1 – x) = cos–1x.
Concept: Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Find the value of a if `[[a-b,2a+c],[2a-b,3c+d]]=[[-1,5],[0,13]]`
Concept: Applications of Determinants and Matrices
Using properties of determinants prove the following: `|[1,x,x^2],[x^2,1,x],[x,x^2,1]|=(1-x^3)^2`
Concept: Properties of Determinants
Using properties of determinants, show that ΔABC is isosceles if:`|[1,1,1],[1+cosA,1+cosB,1+cosC],[cos^2A+cosA,cos^B+cosB,cos^2C+cosC]|=0`
Concept: Properties of Determinants
If A = `([cos alpha, sin alpha],[-sinalpha, cos alpha])` , find α satisfying 0 < α < `pi/r`when `A+A^T=sqrt2I_2` where AT is transpose of A.
Concept: Algebraic Operations on Matrices > Addition of Matrices
Find λ and μ if
`(hati+3hatj+9k)xx(3hati-lambdahatj+muk)=0`
Concept: Determinant of a Square Matrix
Using the properties of determinants, prove the following:
`|[1,x,x+1],[2x,x(x-1),x(x+1)],[3x(1-x),x(x-1)(x-2),x(x+1)(x-1)]|=6x^2(1-x^2)`
Concept: Properties of Determinants
