Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A cylinder containing a gas is lifted from the first floor to the second floor. What is the amount of work done on the gas? What is the amount of work done by the gas? Is the internal energy of the gas increased? Is the temperature of the gas increased?
Solution
As a cylinder is lifted from the first floor to the second floor, there is decrease in the atmospheric pressure on the gas and it expands. Therefore, some work is done by the gas on its surroundings. Work done on the gas is zero.
Work done by the gas, W = PΔV (positive)
The increase in the internal energy and temperature of the system will depend on the types of the walls of the system (conducting or insulating).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is added to it?
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
Consider two processes on a system as shown in figure.
The volumes in the initial states are the same in the two processes and the volumes in the final states are also the same. Let ∆W1 and ∆W2 be the work done by the system in the processes A and B respectively.
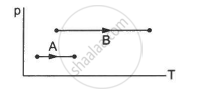
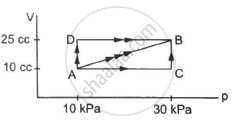
Figure shows three paths through which a gas can be taken from the state A to the state B. Calculate the work done by the gas in each of the three paths.
A mixture of fuel and oxygen is burned in a constant-volume chamber surrounded by a water bath. It was noticed that the temperature of water is increased during the process. Treating the mixture of fuel and oxygen as the system,
- Has heat been transferred?
- Has work been done?
- What is the sign of ∆U?
A system releases 130 kJ of heat while 109 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Explain given cases related to energy transfer between the system and surrounding –
- energy transferred (Q) > 0
- energy transferred (Q) < 0
- energy transferred (Q) = 0
Explain the different ways through which the internal energy of the system can be changed.
In a thermodynamic system, working substance is ideal gas. Its internal energy is in the form of ______.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in the temperature of the gas?
In insulated systems, the amount of external work done by the gas is proportional to:
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
n mole of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) consisting of the following processes:
A `→` B: Isothermal expansion at temperature T so that the volume is doubled from V1 to V2 = 2V1 and pressure changes from P1 to P2.
B `→` C: Isobaric compression at pressure P2 to initial volume V1.
C `→` A: Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from P2 to P1.
Total workdone in the complete cycle ABCA is ______.

A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 50 N/m2 from a volume of 10 m3 to a volume of 4 m3. Energy of 100 J is then added to the gas by heating. Its internal energy is ______.
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
