Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A gas is contained in a metallic cylinder fitted with a piston. The piston is suddenly moved in to compress the gas and is maintained at this position. As time passes the pressure of the gas in the cylinder ______________ .
Options
increases
decreases
remains constant
increases or decreases depending on the nature of the gas
Solution
decreases
As the piston of a metallic cylinder containing gas is moved to compress the gas, the volume in which the gas is contained reduces, leading to increase in pressure and temperature. When the time elapses, the heat generated radiates through the metallic cylinder as metals are good conductors of heat. Consequently, the pressure of the gas in the cylinder decreases because of decrease in the temperature.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the changes in internal energy of the system in the process A and B. Then _____________ .

The pressure p and volume V of an ideal gas both increase in a process.
(a) Such a process is not possible.
(b) The work done by the system is positive.
(c) The temperature of the system must increase.
(d) Heat supplied to the gas is equal to the change in internal energy.
In a process on a system, the initial pressure and volume are equal to the final pressure and volume.
(a) The initial temperature must be equal to the final temperature.
(b) The initial internal energy must be equal to the final internal energy.
(c) The net heat given to the system in the process must be zero.
(d) The net work done by the system in the process must be zero.
A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure. If 2.4 cal of heat is given in the process, what is the value of J ?
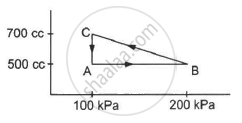
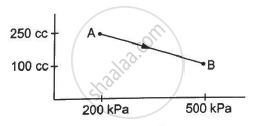
A gas is taken along the path AB as shown in figure. If 70 cal of heat is extracted from the gas in the process, calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
A gas is initially at a pressure of 100 kPa and its volume is 2.0 m3. Its pressure is kept constant and the volume is changed from 2.0 m3 to 2.5 m3. Its Volume is now kept constant and the pressure is increased from 100 kPa to 200 kPa. The gas is brought back to its initial state, the pressure varying linearly with its volume. (a) Whether the heat is supplied to or extracted from the gas in the complete cycle? (b) How much heat was supplied or extracted?
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
When does a system lose energy to its surroundings and its internal energy decreases?
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
In a thermodynamic system, working substance is ideal gas. Its internal energy is in the form of ______.
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
In insulated systems, the amount of external work done by the gas is proportional to:
Figure shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.

- Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II.
- Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases.
- Work done is maximum in case I
- Work done is minimum in case II.
n mole of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) consisting of the following processes:
A `→` B: Isothermal expansion at temperature T so that the volume is doubled from V1 to V2 = 2V1 and pressure changes from P1 to P2.
B `→` C: Isobaric compression at pressure P2 to initial volume V1.
C `→` A: Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from P2 to P1.
Total workdone in the complete cycle ABCA is ______.

If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
The molar specific heat of He at constant volume is 12.47 J/mol.K. Two moles of He are heated at constant pressure. So the rise in temperature is 10 K. Find the increase in internal energy of the gas.
