Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B?
Solution 1
0.5 atm
The volume available to the gas is doubled as soon as the stopcock between cylinders A and B is opened. Since volume is inversely proportional to pressure, the pressure will decrease to one-half of the original value. Since the initial pressure of the gas is 1 atm, the pressure in each cylinder will be 0.5 atm.
Solution 2
Since the final temperature and initial temperature remain the same,
`therefore "P"_2"V"_2 = "P"_1"V"_1`
But P1 = 1 atm, v1 = V, V2 = 2V and P2 = ?
`therefore "P"_2 = ("P"_1"V"_1)/"V"_2 = (1xx"V")/"2V"`
= 0.5 atm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
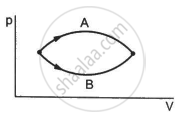
Figure shows two processes A and B on a system. Let ∆Q1 and ∆Q2 be the heat given to the system in processes A and B respectively. Then ____________ .
A 100 kg lock is started with a speed of 2.0 m s−1 on a long, rough belt kept fixed in a horizontal position. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the belt is 0.20. (a) Calculate the change in the internal energy of the block-belt system as the block comes to a stop on the belt. (b) Consider the situation from a frame of reference moving at 2.0 m s−1 along the initial velocity of the block. As seen from this frame, the block is gently put on a moving belt and in due time the block starts moving with the belt at 2.0 m s−1. calculate the increase in the kinetic energy of the block as it stops slipping past the belt. (c) Find the work done in this frame by the external force holding the belt.
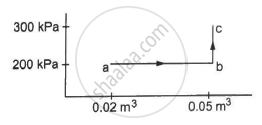
A substance is taken through the process abc as shown in figure. If the internal energy of the substance increases by 5000 J and a heat of 2625 cal is given to the system, calculate the value of J.
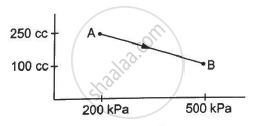
A gas is taken along the path AB as shown in figure. If 70 cal of heat is extracted from the gas in the process, calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
A gas is initially at a pressure of 100 kPa and its volume is 2.0 m3. Its pressure is kept constant and the volume is changed from 2.0 m3 to 2.5 m3. Its Volume is now kept constant and the pressure is increased from 100 kPa to 200 kPa. The gas is brought back to its initial state, the pressure varying linearly with its volume. (a) Whether the heat is supplied to or extracted from the gas in the complete cycle? (b) How much heat was supplied or extracted?
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
An ideal gas is compressed at a constant temperature. Its internal energy will ____________.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
A steam engine delivers 4.8 x 108 Jof work per minute and services 1.2 x 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the percentage efficiency of the engine?
