Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A particle moves in a region with a uniform magnetic field and a parallel, uniform electric field. At some instant, the velocity of the particle is perpendicular to the field direction. The path of the particle will be
Options
a straight line
a circle
a helix with uniform pitch
a helix with non-uniform pitch
Solution
a helix with non-uniform pitch
Here, the total Lorentz force on the particle,
F = qE + qVB
We all know that magnetic field B does not change the speed of the particle but changes its direction. But as an electric field is also present that accelerate the particle in the direction of the field, the resultant path is a helix with a non-uniform pitch.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
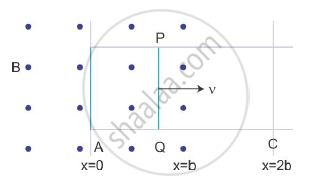
Sketch the change in flux, emf and force when a conducting rod PQ of resistance R and length l moves freely to and fro between A and C with speed v on a rectangular conductor placed in uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure
Can a charged particle be accelerated by a magnetic field? Can its speed be increased?
A vertical wire carries a current in upward direction. An electron beam sent horizontally towards the wire will be deflected
A wire of length l carries a current i long the x-axis. A magnetic field exists, which is given as `vecB = B_0 (veci + vecj + veck)` T. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire.
A current of 5.0 A exists in the circuit shown in the figure. The wire PQ has a length of 50 cm and the magnetic field in which it is immersed has a magnitude of 0.20 T. Find the magnetic force acting on the wire PQ.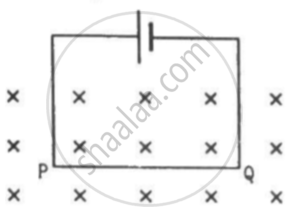
Consider a non-conducting plate of radius r and mass m that has a charge q distributed uniformly over it. The plate is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. Show that the magnetic moment µ and the angular momentum l of the plate are related as `mu = q/(2 m)l`
A long wire carrying a current i is bent to form a place along α . Find the magnetic field B at a point on the bisector of this angle situated at a distance x from the vertex.
Figure shows a part of an electric circuit. The wires AB, CD and EF are long and have identical resistance. The separation between the neighbouring wires is 1.0 cm. The wires AE and BF have negligible resistance and the ammeter reads 30 A. Calculate the magnetic force per unit length of AB and CD.

A long, straight wire is fixed horizontally and carries a current of 50.0 A. A second wire having linear mass density 1.0 × 10−4 kg m−1 is placed parallel to and directly above this wire at a separation of 5.0 mm. What current should this second wire carry such that the magnetic repulsion can balance its weight?
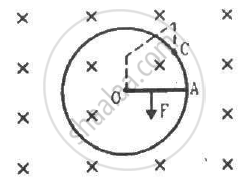
Consider the situation shown in the figure. Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. Find the magnitude of this force when the rod makes an angle θ with the vertical.
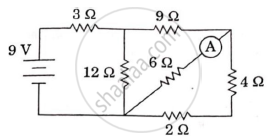
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the value of the current shown in the ammeter A.
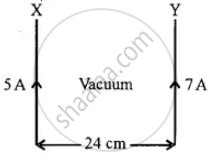
Two infinitely long current carrying conductors X and Y are kept parallel to each other, 24 cm apart in a vacuum. They carry currents of 5A and 7A respectively, in the same direction, as shown in the figure below. Find the position of a neutral point, i.e., a point where resultant magnetic flux density is zero. (Ignore earth’s magnetic field).
A straight horizontal conducting rod of length 0.45 m and mass 60 g is suspended by two vertical wires at its ends. A current of 5.0 A is set up in the rod through the wires.
(a) What magnetic field should be set up normal to the conductor in order that the tension in the wires is zero?
(b) What will be the total tension in the wires if the direction of current is reversed keeping the magnetic field same as before?
(Ignore the mass of the wires) g = 9.8 m s–2.
A charged particle is moving on circular path with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B, if the velocity of the charged particle is doubled and strength of magnetic field is halved, then radius becomes ______.
A current of 3 A is flowing in a linear conductor having a length of 40 cm. The conductor is placed in a magnetic field of strength of 500 gauss and makes an angle of 30° with the direction of the field. It experiences a force of magnitude:
A straight conductor of length 2m moves at a speed of 20 m/s. When the conductor makes an angle of 30° with the direction of magnetic field of induction of 0.1 wbm2 then induced emf:
A conducting ring of radius 1m kept in a uniform magnetic field B of 0.01 T, rotates uniformly with an angular velocity 100 rad s−1 with its axis of rotation perpendicular to B. The maximum induced emf in it is:
