Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A steel rod 100 cm long is clamped at its middle. The fundamental frequency of longitudinal vibrations of the rod is given to be 2.53 kHz. What is the speed of sound in steel?
Solution 1
Length of the steel rod, l = 100 cm = 1 m
Fundamental frequency of vibration, ν = 2.53 kHz = 2.53 × 103 Hz
When the rod is plucked at its middle, an antinode (A) is formed at its centre, and nodes (N) are formed at its two ends, as shown in the given figure.
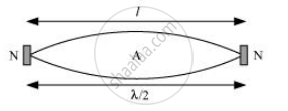
The distance between two successive nodes is `pi/2`
`:. l = lambda/2`
`lambda = 2l = 2x 1 = 2m`
The speed of sound in steel is given by the relation:
v = νλ
= 2.53 × 103 × 2
= 5.06 × 103 m/s
= 5.06 km/s
Solution 2
Here, L = 100 cm = 1m, v = 2.53 k Hz = 2.53 x 103 Hz
When the rod is clamped at the middle, then in the fundamental mode of vibration of the rod, a node is formed at the middle and ant mode is formed at each end.
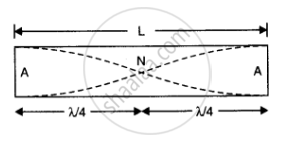
Therefore as is clear from figure
`L= lambda/4 + lambda/4 = lambda/2`
`lambda = 2 L= 2 m`
As `v = vlambda`
`:. v = 2.53 xx 10^3 xx 2`
`= 5.06 xx 10^3 ms^(-1)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A train, standing at the outer signal of a railway station blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz in still air. (i) What is the frequency of the whistle for a platform observer when the train (a) approaches the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1, (b) recedes from the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1? (ii) What is the speed of sound in each case? The speed of sound in still air can be taken as 340 m s–1.
A sonometer wire of length l vibrates in fundamental mode when excited by a tuning fork of frequency 416. Hz. If the length is doubled keeping other things same, the string will ______.
The displacement of the particle at x = 0 of a stretched string carrying a wave in the positive x-direction is given f(t) = A sin (t/T). The wave speed is v. Write the wave equation.
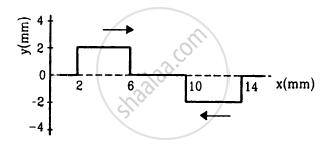
Following figure shows two wave pulses at t = 0 travelling on a string in opposite directions with the same wave speed 50 cm s−1. Sketch the shape of the string at t = 4 ms, 6 ms, 8 ms, and 12 ms.
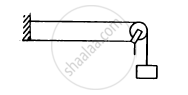
Following figure shows a string stretched by a block going over a pulley. The string vibrates in its tenth harmonic in unison with a particular tuning for. When a beaker containing water is brought under the block so that the block is completely dipped into the beaker, the string vibrates in its eleventh harmonic. Find the density of the material of the block.
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of `λ/2`.
Speed of sound wave in air ______.
If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
An engine is approaching a cliff at a constant speed. When it is at a distance of 0.9 km from cliff it sounds a whistle. The echo of the sound is heard by the driver after 5 seconds. Velocity of sound in air is equal to 330 ms-1. The speed of the engine is ______ km/h.
The displacement y of a particle in a medium can be expressed as, y = `10^-6sin(100t + 20x + pi/4)` m where t is in second and x in meter. The speed of the wave is ______.
