Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A uniform metal sphere of radius a and mass M is surrounded by a thin uniform spherical shell of equal mass and radius 4a (In the following figure). The centre of the shell falls on the surface of the inner sphere. Find the gravitational field at the points P1 and P2 shown in the figure.
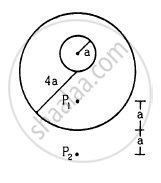
Solution
At point P1, the gravitational field due to the sphere and the shell is given by
F \[= \frac{GM}{\left( 3a + a \right)^2} + 0 = \frac{GM}{16 a^2}\]
At point P2, the gravitational field due to the sphere and the shell is given by
\[F = \frac{GM}{\left( a + 4a + a \right)^2} + \frac{GM}{\left( 4a + a \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \frac{GM}{36 a^2} + \frac{GM}{25 a^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \frac{GM}{a^2}\left( \frac{1}{36} + \frac{1}{25} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \frac{GM}{a^2}\left( \frac{25 + 36}{900} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \left( \frac{61}{900} \right)\frac{GM}{a^2}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 106 m).
Answer the following:
You can shield a charge from electrical forces by putting it inside a hollow conductor. Can you shield a body from the gravitational influence of nearby matter by putting it inside a hollow sphere or by some other means?
If you compare the gravitational force on the Earth due to the Sun to that due to the Moon, you would find that the Sun’s pull is greater than the Moon’s pull. (You can check this yourself using the data available in the succeeding exercises). However, the tidal effect of the Moon’s pull is greater than the tidal effect of Sun. Why?
Choose the correct alternative:
Acceleration due to gravity is independent of mass of the earth/mass of the body.
A person brings a mass of 1 kg from infinity to a point A. Initially the mass was at rest but it moves at a speed of 2 m s −1 as it reaches A. The work done by the person on the mass is −3 J. The potential at A is
A body is suspended from a spring balance kept in a satellite. The reading of the balance is W1 when the satellite goes in an orbit of radius R and is W2 when it goes in an orbit of radius 2 −R.
Two spherical balls of mass 10 kg each are placed 10 cm apart. Find the gravitational force of attraction between them.
Explain the following:
People often shake the branches of a tree for getting down its fruits.
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Made four times
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Infinite
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case:
A book lying on a table.
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case:
Hammering a nail.
Explain the difference between g and G.
State Newton's law of gravitation. What is the difference between:
g and G?
The distance-time values for an object moving along straight line are given below:
| Time (s) | Distance (m) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 27 |
Show that gravity decreases at higher altitudes.
The force of gravitation between two bodies of mass 1 kg each separated by a distance of 1 m in vacuum is ____________.
Shown are several curves (Figure). Explain with reason, which ones amongst them can be possible trajectories traced by a projectile (neglect air friction).
Six point masses of mass m each are at the vertices of a regular hexagon of side l. Calculate the force on any of the masses.
Observe the figure and answer the questions:
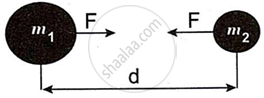
- State Newton's universal law of gravitation.
- If the distance between the two bodies is tripled, how will the gravitational force between them change?
- What will happen to gravitational force, if mass of one of the object is doubled?
