Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the figure and answer the questions:
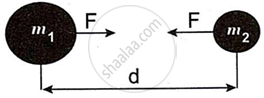
- State Newton's universal law of gravitation.
- If the distance between the two bodies is tripled, how will the gravitational force between them change?
- What will happen to gravitational force, if mass of one of the object is doubled?
Solution
- According to Newton’s universal law of gravitation theory, every object in the universe attracts every other object with a definite force. This force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The above figure shows two objects with masses m1 and m2 kept at a distance d from each other. Mathematically, the gravitational force of attraction between these two bodies can be written as
`Fα (m_1m_2)/d^2 or F= G (m_1m_2)/d^2`
Here, G is the constant of proportionality and is called the universal gravitational constant. - If the distance between the two bodies is tripled, the gravitational force between them would decrease by a factor of 9 (since force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance). This is because according to the law of gravitation, F ∝ `1/d^2`, so if d becomes 3d, then
`F = G(m_1m_2)/(3d^2) = G(m_1m_2)/(9d^2)` - If the mass of one of the objects is doubled, the gravitational force between them will also double. This is because the force is directly proportional to the masses of the objects. So, F ∝ m1 or F ∝ m2, which means if m1 becomes 2m1,
`F = G(2m_1m_2)/(d^2) = 2G(m_1m_2)/(d^2)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 106 m).
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
How will you ‘weigh the sun’, that is estimate its mass? The mean orbital radius of the earth around the sun is 1.5 × 108 km.
State Kepler’s law which is represented by the relation r3 ∝ T2.
Three uniform spheres each having a mass M and radius a are kept in such a way that each touches the other two. Find the magnitude of the gravitational force on any of the spheres due to the other two.
The law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between :
All objects in the universe attract each other along the line joining their________.
Where will you weigh more: at the centre of the earth or at the surface of the earth?
What is meant by the equation :
`g= Gxxm/r^2`
where the symbols have their usual meanings.
At what height above the earth's surface would the value of acceleration due to gravity be half of what it is on the surface? Take the radius of earth to be R.
A force can produce ________, In an object at rest. It can __________ an object and change its __________ of motion.
What does a force do in the following case?
You apply brakes to a running car.
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case:
A person walking on the ground.
What is the difference between gravity and gravitation?
Does the force of the earth's gravitation affect the motion of the moon? Explain your answer with reasons.
An apple falls towards the earth due to its gravitational force. The apple also attracts the earth with the same force. Why do we not see the earth rising towards the apple? Explain.
Give scientific reasons for the following:
Newton's gravitational law is the universal law of gravitation.
Two particles of equal mass 'm' go around a circle of radius R under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. The speed of each particle with respect to its centre of mass is ______.
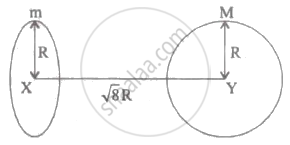
Find the gravitational force of attraction between the ring and sphere as shown in the diagram, where the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres. If `sqrt8` R is the distance between the centres of a ring (of mass 'm')and a sphere (mass 'M') where both have equal radius 'R'.