Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A wholesale dealer deals in two kinds, A and B (say) of mixture of nuts. Each kg of mixture A contains 60 grams of almonds, 30 grams of cashew nuts and 30 grams of hazel nuts. Each kg of mixture B contains 30 grams of almonds, 60 grams of cashew nuts and 180 grams of hazel nuts. The remainder of both mixtures is per nuts. The dealer is contemplating to use mixtures A and B to make a bag which will contain at least 240 grams of almonds, 300 grams of cashew nuts and 540 grams of hazel nuts. Mixture A costs Rs 8 per kg. and mixture B costs Rs 12 per kg. Assuming that mixtures A and B are uniform, use graphical method to determine the number of kg. of each mixture which he should use to minimise the cost of the bag.
Solution
Let x kg of kind A and y kg of kind B were used.
Quantity cannot be negative.
Therefore,
The given information can be tabulated as follows:
| Nut | Almonds(grams) | Cashewnuts(grams) | Hazel nuts(grams) |
| A(x) | 60 | 30 | 30 |
| B(y) | 30 | 60 | 180 |
| Availability | 240 | 300 | 540 |
Therefore, the constraints are
\[60x + 30y \geq 240\]
\[30x + 60y \geq 300\]
\[30x + 180y \geq 540\]
Mixture A costs Rs 8 per kg. and mixture B costs Rs 12 per kg.
Total cost = Z = \[8x + 12y\]
which is to be minimised.
Thus, the mathematical formulation of the given linear programmimg problem is
Min Z = \[8x + 12y\] subject to
\[2x + y \geq 8\]
\[ x + 2y \geq 10\]
\[ x + 6y \geq 18\]
First, we will convert the given inequations into equations, we obtain the following equations:
2x + y = 8, x +2y = 10, x +6y = 18, x = 0 and y = 0
Region represented by 2x + y ≥ 8:
The line 2x + y = 8 meets the coordinate axes at A1(4, 0) and B1(0, 8) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line 2x + y = 8.
Clearly (0,0) does not satisfies the inequation 2x + y ≥ 8. So,the region in xy plane which does not contain the origin represents the solution set of the inequation 2x + y ≥ 8.
Region represented by x +2y ≥ 10:
The line x +2y = 10 meets the coordinate axes at C1(10,0) and D1(0, 5) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line
x +2y = 10. Clearly (0,0) does not satisfies the inequation x +2y ≥ 10. So,the region which does not contain the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x +2y ≥ 10.
Region represented by x +6y ≥ 18:
The line x +6y = 18 meets the coordinate axes at E1(18,0) and F1(0, 3) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line x + 6y = 18.Clearly (0,0) does not satisfies the inequation x + 6y ≥ 18. So,the region which does not contain the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x +6y ≥ 18.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints 2x + y ≥ 8, x + 2y ≥ 10,x + 6y ≥ 18, x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0, are as follows.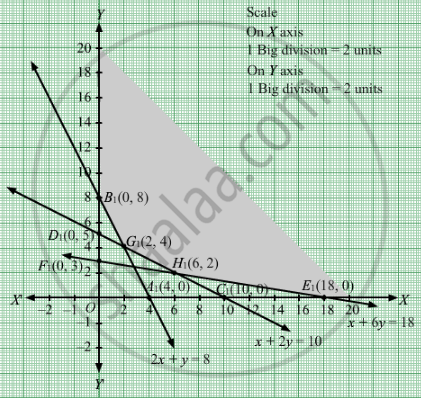 The corner points are B1(0, 8), G1(2, 4), H1(6, 2) and E1(18, 0).
The corner points are B1(0, 8), G1(2, 4), H1(6, 2) and E1(18, 0).
The values of Z at these corner points are as follows
| Corner point | Z= 8x + 12y |
| B1 | 96 |
| G1 | 64 |
| H1 | 72 |
| E1 | 144 |
The minimum value of Z is 64 which is attained at G1
Thus, the minimum cost is Rs 64 obtained when 2 units of kind A and 4 units of kind B nuts were used.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A manufacturer produces two products A and B. Both the products are processed on two different machines. The available capacity of first machine is 12 hours and that of second machine is 9 hours per day. Each unit of product A requires 3 hours on both machines and each unit of product B requires 2 hours on first machine and 1 hour on second machine. Each unit of product A is sold at Rs 7 profit and B at a profit of Rs 4. Find the production level per day for maximum profit graphically.
Solve the following L.P.P graphically: Maximise Z = 20x + 10y
Subject to the following constraints x + 2y ≤ 28,
3x + y ≤ 24,
x ≥ 2,
x, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Minimize Z = 7x + y subject to 5x + y ≥ 5, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
In order to supplement daily diet, a person wishes to take X and Y tablets. The contents (in milligrams per tablet) of iron, calcium and vitamins in X and Y are given as below :
| Tablets | Iron | Calcium | Vitamin |
| x | 6 | 3 | 2 |
| y | 2 | 3 | 4 |
The person needs to supplement at least 18 milligrams of iron, 21 milligrams of calcium and 16 milligrams of vitamins. The price of each tablet of X and Y is Rs 2 and Rs 1 respectively. How many tablets of each type should the person take in order to satisfy the above requirement at the minimum cost? Make an LPP and solve graphically.
Maximize Z = 15x + 10y
Subject to
\[3x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 3y \leq 70\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 2x + 4y
Subject to
\[x + y \geq 8\]
\[x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[x \geq 3, y \geq 2\]
Minimize Z = 30x + 20y
Subject to
\[x + y \leq 8\]
\[ x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[5x + 8y = 20\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 4x + 3y
Subject to
\[3x + 4y \leq 24\]
\[8x + 6y \leq 48\]
\[ x \leq 5\]
\[ y \leq 6\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 3x1 + 5x2
Subject to
\[x_1 + 3 x_2 \geq 3\]
\[ x_1 + x_2 \geq 2\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = x + y
Subject to
\[- 2x + y \leq 1\]
\[ x \leq 2\]
\[ x + y \leq 3\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2, if possible,
Subject to the constraints
\[x_1 - x_2 \leq - 1\]
\[ - x_1 + x_2 \leq 0\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Show the solution zone of the following inequalities on a graph paper:
\[5x + y \geq 10\]
\[ x + y \geq 6\]
\[x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[x \geq 0, y \geq 0\]
Find x and y for which 3x + 2y is minimum subject to these inequalities. Use a graphical method.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimize z = 6 x + 3 y
Subject to the constraints:
4 x + \[y \geq\] 80
x + 5 \[y \geq\] 115
3 x + 2 \[y \leq\] 150
\[x \geq\] 0 , \[y \geq\] 0
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs ₹60/kg and food Q costs ₹80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/kg of vitamin A and 5 units/kg of vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food X and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B and 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Y | 2 | 2 | 1 |
One kg of food X costs ₹16 and one kg of food Y costs ₹20. Find the least cost of the mixture which will produce the required diet?
Two tailors, A and B earn Rs 15 and Rs 20 per day respectively. A can stitch 6 shirts and 4 pants while B can stitch 10 shirts and 4 pants per day. How many days shall each work if it is desired to produce (at least) 60 shirts and 32 pants at a minimum labour cost?
A firm manufacturing two types of electric items, A and B, can make a profit of Rs 20 per unit of A and Rs 30 per unit of B. Each unit of A requires 3 motors and 4 transformers and each unit of B requires 2 motors and 4 transformers. The total supply of these per month is restricted to 210 motors and 300 transformers. Type B is an export model requiring a voltage stabilizer which has a supply restricted to 65 units per month. Formulate the linear programing problem for maximum profit and solve it graphically.
A firm manufactures headache pills in two sizes A and B. Size A contains 2 grains of aspirin, 5 grains of bicarbonate and 1 grain of codeine; size B contains 1 grain of aspirin, 8 grains of bicarbonate and 66 grains of codeine. It has been found by users that it requires at least 12 grains of aspirin, 7.4 grains of bicarbonate and 24 grains of codeine for providing immediate effects. Determine graphically the least number of pills a patient should have to get immediate relief. Determine also the quantity of codeine consumed by patient.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend ₹2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to ₹5 per km. He has ₹100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A library has to accommodate two different types of books on a shelf. The books are 6 cm and 4 cm thick and weigh 1 kg and \[1\frac{1}{2}\] kg each respectively. The shelf is 96 cm long and atmost can support a weight of 21 kg. How should the shelf be filled with the books of two types in order to include the greatest number of books? Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type A which contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and of type B which contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After the soil test, it is found that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and the same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type A costs ₹ 5.00 per kg and the type B costs ₹ 8.00 per kg. Using Linear programming, find how many kilograms of each type of fertilizer should be bought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph.
Find the solution set of inequalities 0 ≤ x ≤ 5, 0 ≤ 2y ≤ 7
Draw the graph of inequalities x ≤ 6, y −2 ≤ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 and indicate the feasible region
Maximum value of 4x + 13y subject to constraints x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, x + y ≤ 5 and 3x + y ≤ 9 is ______.
For the LPP, maximize z = x + 4y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 2, x + 2y ≥ 8, x, y ≥ 0 ______.
The constraints of an LPP are 7 ≤ x ≤ 12, 8 ≤ y ≤ 13. Determine the vertices of the feasible region formed by them.
Maximise and Minimise Z = 3x – 4y subject to x – 2y ≤ 0, – 3x + y ≤ 4, x – y ≤ 6, x, y ≥ 0
Let R be the feasible region (convex polygon) for a linear programming problem and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. When Z has an optimal value (maximum or minimum), where the variables x and y are subject to constraints described by linear inequalities,
Let R be the feasible region for a linear programming problem, and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. If R is bounded, then the objective function Z has both a maximum and a minimum value on R and ____________.
Which of the statements describe the solution set for `-2(x + 8) = - 2x + 20`?
Any point in the feasible region that gives the optional value (maximum or minimum) of the objective function is called:-
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize Z = 400x + 300y subject to x + y ≤ 200, x ≤ 40, x ≥ 20, y ≥ 0
The maximum value of 2x + y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26 and 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The shaded part of given figure indicates in feasible region, then the constraints are:

Draw the rough graph and shade the feasible region for the inequalities x + y ≥ 2, 2x + y ≤ 8, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
