Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw the graph of inequalities x ≤ 6, y −2 ≤ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 and indicate the feasible region
Solution
| Given inequalities | x ≤ 6 | y – 2 ≤ 0 |
| Corresponding equalities | x = 6 | y = 2 |
| Intersection of line with X-axis | A(6, 0) | Parallel to X-axis |
| Intersection of line with Y-axis | Parallel to Y-axis | Parallel to Y-axis |
| Origin test |
0 ≤ 6 which is true |
2 ≤ 0 which is true |
| Region | Origin side of the line | Origin side of the line |
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 represent 1st quadrant.
The shaded portion represents the feasible solution.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Solve the following LPP by using graphical method.
Maximize : Z = 6x + 4y
Subject to x ≤ 2, x + y ≤ 3, -2x + y ≤ 1, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Also find maximum value of Z.
Solve the following L.P.P graphically:
Maximize: Z = 10x + 25y
Subject to: x ≤ 3, y ≤ 3, x + y ≤ 5, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
There are two types of fertilisers 'A' and 'B'. 'A' consists of 12% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid whereas 'B' consists of 4% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops. If 'A' costs Rs 10 per kg and 'B' cost Rs 8 per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost
Find graphically, the maximum value of z = 2x + 5y, subject to constraints given below :
2x + 4y ≤ 83
x + y ≤ 6
x + y ≤ 4
x ≥ 0, y≥ 0
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y
Subject to: x + 4y ≤ 24
3x + y ≤ 21
x + y ≤ 9
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Maximise Z = x + 2y subject to the constraints
`x + 2y >= 100`
`2x - y <= 0`
`2x + y <= 200`
Solve the above LPP graphically
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically:
Minimise Z = 5x + 10y
Subject to x + 2y ≤ 120
Constraints x + y ≥ 60
x – 2y ≥ 0 and x, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP graphically :
Maximise Z = 105x + 90y
subject to the constraints
x + y ≤ 50
2x + y ≤ 80
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 5x + 3y
Subject to
\[3x + 5y \leq 15\]
\[5x + 2y \leq 10\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 9x + 3y
Subject to
\[2x + 3y \leq 13\]
\[ 3x + y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x + 4y
Subject to
\[2x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 4y \leq 120\]
Minimize Z = x − 5y + 20
Subject to
\[x - y \geq 0\]
\[ - x + 2y \geq 2\]
\[ x \geq 3\]
\[ y \leq 4\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 3x1 + 5x2
Subject to
\[x_1 + 3 x_2 \geq 3\]
\[ x_1 + x_2 \geq 2\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = x + y
Subject to
\[- 2x + y \leq 1\]
\[ x \leq 2\]
\[ x + y \leq 3\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2, if possible,
Subject to the constraints
\[x_1 - x_2 \leq - 1\]
\[ - x_1 + x_2 \leq 0\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Find the maximum and minimum value of 2x + y subject to the constraints:
x + 3y ≥ 6, x − 3y ≤ 3, 3x + 4y ≤ 24, − 3x + 2y ≤ 6, 5x + y ≥ 5, x, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimize z = 6 x + 3 y
Subject to the constraints:
4 x + \[y \geq\] 80
x + 5 \[y \geq\] 115
3 x + 2 \[y \leq\] 150
\[x \geq\] 0 , \[y \geq\] 0
A diet for a sick person must contain at least 4000 units of vitamins, 50 units of minerals and 1400 of calories. Two foods A and B, are available at a cost of Rs 4 and Rs 3 per unit respectively. If one unit of A contains 200 units of vitamin, 1 unit of mineral and 40 calories and one unit of food B contains 100 units of vitamin, 2 units of minerals and 40 calories, find what combination of foods should be used to have the least cost?
A hospital dietician wishes to find the cheapest combination of two foods, A and B, that contains at least 0.5 milligram of thiamin and at least 600 calories. Each unit of Acontains 0.12 milligram of thiamin and 100 calories, while each unit of B contains 0.10 milligram of thiamin and 150 calories. If each food costs 10 paise per unit, how many units of each should be combined at a minimum cost?
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs ₹60/kg and food Q costs ₹80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/kg of vitamin A and 5 units/kg of vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
One kind of cake requires 200 g of flour and 25 g of fat, and another kind of cake requires 100 g of flour and 50 g of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from 5 kg of flour and 1 kg of fat assuming that there is no storage of the other ingredients used in making the cakes.
A farmer mixes two brands P and Q of cattle feed. Brand P, costing ₹250 per bag, contains 2 units of nutritional element A, 2.5 units of element B and 2 units of element C. Brand Q costing ₹200 per bag contains 1.5 units of nutritional element A, 11.25 units of element B and 3 units of element C. The minimum requirements of nutrients A, B and C are 18 units, 45 units and 24 units respectively. Determine the number of bags of each brand which should be mixed in order to produce a mixture having a minimum cost per bag? What is the minimum cost of the mixture per bag?
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend Rs 2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to Rs 5/per km. He has Rs 100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A manufacturer has three machines installed in his factory. machines I and II are capable of being operated for at most 12 hours whereas Machine III must operate at least for 5 hours a day. He produces only two items, each requiring the use of three machines. The number of hours required for producing one unit each of the items on the three machines is given in the following table:
| Item | Number of hours required by the machine | ||
A B |
I | II | III |
| 1 2 |
2 1 |
1 5/4 |
|
He makes a profit of Rs 6.00 on item A and Rs 4.00 on item B. Assuming that he can sell all that he produces, how many of each item should he produces so as to maximize his profit? Determine his maximum profit. Formulate this LPP mathematically and then solve it.
A factory manufactures two types of screws, A and B, each type requiring the use of two machines - an automatic and a hand-operated. It takes 4 minute on the automatic and 6 minutes on the hand-operated machines to manufacture a package of screws 'A', while it takes 6 minutes on the automatic and 3 minutes on the hand-operated machine to manufacture a package of screws 'B'. Each machine is available for at most 4 hours on any day. The manufacturer can sell a package of screws 'A' at a profit of 70 P and screws 'B' at a profit of Rs 1. Assuming that he can sell all the screws he can manufacture, how many packages of each type should the factory owner produce in a day in order to maximize his profit? Determine the maximum profit.
A company produces two types of leather belts, say type A and B. Belt A is a superior quality and belt B is of a lower quality. Profits on each type of belt are Rs 2 and Rs 1.50 per belt, respectively. Each belt of type A requires twice as much time as required by a belt of type B. If all belts were of type B, the company could produce 1000 belts per day. But the supply of leather is sufficient only for 800 belts per day (both A and B combined). Belt A requires a fancy buckle and only 400 fancy buckles are available for this per day. For belt of type B, only 700 buckles are available per day.
How should the company manufacture the two types of belts in order to have a maximum overall profit?
A small manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes an article in two qualities deluxe model and an ordinary model. The making of a deluxe model requires 2 hrs. work by a skilled man and 2 hrs. work by a semi-skilled man. The ordinary model requires 1 hr by a skilled man and 3 hrs. by a semi-skilled man. By union rules no man may work more than 8 hrs per day. The manufacturers clear profit on deluxe model is Rs 15 and on an ordinary model is Rs 10. How many of each type should be made in order to maximize his total daily profit.
A furniture manufacturing company plans to make two products : chairs and tables. From its available resources which consists of 400 square feet to teak wood and 450 man hours. It is known that to make a chair requires 5 square feet of wood and 10 man-hours and yields a profit of Rs 45, while each table uses 20 square feet of wood and 25 man-hours and yields a profit of Rs 80. How many items of each product should be produced by the company so that the profit is maximum?
A firm manufactures two products A and B. Each product is processed on two machines M1 and M2. Product A requires 4 minutes of processing time on M1 and 8 min. on M2 ; product B requires 4 minutes on M1 and 4 min. on M2. The machine M1 is available for not more than 8 hrs 20 min. while machine M2 is available for 10 hrs. during any working day. The products A and B are sold at a profit of Rs 3 and Rs 4 respectively.
Formulate the problem as a linear programming problem and find how many products of each type should be produced by the firm each day in order to get maximum profit.
A publisher sells a hard cover edition of a text book for Rs 72.00 and paperback edition of the same ext for Rs 40.00. Costs to the publisher are Rs 56.00 and Rs 28.00 per book respectively in addition to weekly costs of Rs 9600.00. Both types require 5 minutes of printing time, although hardcover requires 10 minutes binding time and the paperback requires only 2 minutes. Both the printing and binding operations have 4,800 minutes available each week. How many of each type of book should be produced in order to maximize profit?
A firm manufactures headache pills in two sizes A and B. Size A contains 2 grains of aspirin, 5 grains of bicarbonate and 1 grain of codeine; size B contains 1 grain of aspirin, 8 grains of bicarbonate and 66 grains of codeine. It has been found by users that it requires at least 12 grains of aspirin, 7.4 grains of bicarbonate and 24 grains of codeine for providing immediate effects. Determine graphically the least number of pills a patient should have to get immediate relief. Determine also the quantity of codeine consumed by patient.
A company manufactures two types of novelty Souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type A require 5 minutes each for cutting and 10 minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type B require 8 minutes each for cutting and 8 minutes each for assembling. There are 3 hours 20 minutes available for cutting and 4 hours available for assembling. The profit is 50 paise each for type A and 60 paise each for type B souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should the company manufacture in order to maximize the profit?
A manufacturer makes two products A and B. Product A sells at Rs 200 each and takes 1/2 hour to make. Product B sells at Rs 300 each and takes 1 hour to make. There is a permanent order for 14 of product A and 16 of product B. A working week consists of 40 hours of production and weekly turnover must not be less than Rs 10000. If the profit on each of product A is Rs 20 and on product B is Rs 30, then how many of each should be produced so that the profit is maximum. Also, find the maximum profit.
A manufacturer produces two types of steel trunks. He has two machines A and B. For completing, the first types of the trunk requires 3 hours on machine A and 3 hours on machine B, whereas the second type of the trunk requires 3 hours on machine A and 2 hours on machine B. Machines A and B can work at most for 18 hours and 15 hours per day respectively. He earns a profit of Rs 30 and Rs 25 per trunk of the first type and the second type respectively. How many trunks of each type must he make each day to make maximum profit?
A gardener has supply of fertilizer of type I which consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and type II fertilizer which consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, he finds that he needs at least 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for his crop. If the type I fertilizer costs 60 paise per kg and type II fertilizer costs 40 paise per kg, determine how many kilograms of each fertilizer should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
A small firm manufacturers items A and B. The total number of items A and B that it can manufacture in a day is at the most 24. Item A takes one hour to make while item B takes only half an hour. The maximum time available per day is 16 hours. If the profit on one unit of item A be Rs 300 and one unit of item B be Rs 160, how many of each type of item be produced to maximize the profit? Solve the problem graphically.
A company manufactures two articles A and B. There are two departments through which these articles are processed: (i) assembly and (ii) finishing departments. The maximum capacity of the first department is 60 hours a week and that of other department is 48 hours per week. The product of each unit of article A requires 4 hours in assembly and 2 hours in finishing and that of each unit of B requires 2 hours in assembly and 4 hours in finishing. If the profit is Rs 6 for each unit of A and Rs 8 for each unit of B, find the number of units of A and B to be produced per week in order to have maximum profit.
A firm makes items A and B and the total number of items it can make in a day is 24. It takes one hour to make an item of A and half an hour to make an item of B. The maximum time available per day is 16 hours. The profit on an item of A is Rs 300 and on one item of B is Rs 160. How many items of each type should be produced to maximize the profit? Solve the problem graphically.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend ₹2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to ₹5 per km. He has ₹100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
An oil company has two depots, A and B, with capacities of 7000 litres and 4000 litres respectively. The company is to supply oil to three petrol pumps, D, E, F whose requirements are 4500, 3000 and 3500 litres respectively. The distance (in km) between the depots and petrol pumps is given in the following table:
Figure
Assuming that the transportation cost per km is Rs 1.00 per litre, how should the delivery be scheduled in order that the transportation cost is minimum?
A small firm manufactures gold rings and chains. The total number of rings and chains manufactured per day is at most 24. It takes 1 hour to make a ring and 30 minutes to make a chain. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a ring is Rs 300 and that on a chain is Rs 190, find the number of rings and chains that should be manufactured per day, so as to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes 1.5 hours of machine time and 3 hours of craftman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes 3 hours of machine time and 1 hour of craftman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than 42 hours of machine time and 24 hours of craftman's time. If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs 20 and Rs 10 respectively, find the number of tennis rackets and cricket bats that the factory must manufacture to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A manufacturing company makes two models A and B of a product. Each piece of model A requires 9 labour hours for fabricating and 1 labour hour for finishing. Each piece of model B requires 12 labour hours for fabricating and 3 labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available are 180 and 30 respectively. The company makes a profit of ₹8000 on each piece of model A and ₹12000 on each piece of model B. How many pieces of model A and model B should be manufactured per week to realise a maximum profit? What is the maximum profit per week?
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes 1.5 hours of machine time and 3 hours of craftman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes 3 hours of machine time and 1 hour of craftman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than 42 hours of machine time and 24 hours of craftman's time.
(i) What number of rackets and bats must be made if the factory is to work at full capacity?
(ii) If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs 20 and Rs 10 respectively, find the maximum profit of the factory when it works at full capacity.
A manufacturer produces two products A and B. Both the products are processed on two different machines. The available capacity of first machine is 12 hours and that of second machine is 9 hours per day. Each unit of product A requires 3 hours on both machines and each unit of product B requires 2 hours on first machine and 1 hour on second machine. Each unit of product A is sold at ₹7 profit and that of B at a profit of ₹4. Find the production level per day for maximum profit graphically.
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most 24. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a necklace is Rs 100 and that on a bracelet is Rs 300. Formulate on L.P.P. for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximize the profit?
It is being given that at least one of each must be produced.
By graphical method, the solution of linear programming problem
\[\text{ Subject } to \text{ 3 } x_1 + 2 x_2 \leq 18\]
\[ x_1 \leq 4\]
\[ x_2 \leq 6\]
\[ x_1 \geq 0, x_2 \geq 0, \text{ is } \]
The value of objective function is maximum under linear constraints ______.
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type A which contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and of type B which contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After the soil test, it is found that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and the same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type A costs ₹ 5.00 per kg and the type B costs ₹ 8.00 per kg. Using Linear programming, find how many kilograms of each type of fertilizer should be bought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph.
From the details given below, calculate the five-year moving averages of the number of students who have studied in a school. Also, plot these and original data on the same graph paper.
| Year | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| Number of Students | 332 | 317 | 357 | 392 | 402 | 405 | 410 | 427 | 405 | 438 |
A manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes two models A and B of an article. The making of one item of model A requires 2 hours of work by a skilled man and 2 hours work by a semi-skilled man. One item of model B requires 1 hour by a skilled man and 3 hours by a semi-skilled man. No man is expected to work more than 8 hours per day. The manufacturer's profit on an item of model A is ₹ 15 and on an item of model B is ₹ 10. How many items of each model should be made per day in order to maximize daily profit? Formulate the above LPP and solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
Find the solution set of inequalities 0 ≤ x ≤ 5, 0 ≤ 2y ≤ 7
For L.P.P. maximize z = 4x1 + 2x2 subject to 3x1 + 2x2 ≥ 9, x1 - x2 ≤ 3, x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0 has ______.
The region XOY - plane which is represented by the inequalities -5 ≤ x ≤ 5, -5 ≤ y ≤ 5 is ______
The maximum value of z = 3x + 10y subjected to the conditions 5x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + 5y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
If 4x + 5y ≤ 20, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, maximum 2x + 3y is ______.
The maximum of z = 5x + 2y, subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The minimum value of z = 7x + 9y subject to 3x + y ≤ 6, 5x + 8y ≤ 40, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 2 is ______.
The feasible region (shaded) for a L.P.P is shown in the figure. The maximum Z = 5x + 7y is ____________.
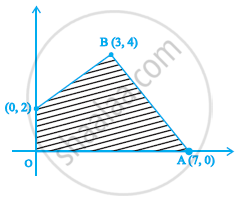
The maximum value of Z = 3x + 4y subjected to contraints x + y ≤ 40, x + 2y ≤ 60, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 is ____________.
The maximum value of z = 5x + 2y, subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The shaded part of given figure indicates in feasible region, then the constraints are:

The objective function Z = ax + by of an LPP has maximum vaiue 42 at (4, 6) and minimum value 19 at (3, 2). Which of the following is true?
The corner points of the feasible region of a linear programming problem are (0, 4), (8, 0) and `(20/3, 4/3)`. If Z = 30x + 24y is the objective function, then (maximum value of Z – minimum value of Z) is equal to ______.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: P = 70x + 40y
Subject to: 3x + 2y ≤ 9,
3x + y ≤ 9,
x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0.
The feasible region corresponding to the linear constraints of a Linear Programming Problem is given below.
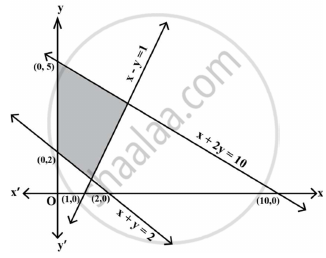
Which of the following is not a constraint to the given Linear Programming Problem?
If x – y ≥ 8, x ≥ 3, y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 then find the coordinates of the corner points of the feasible region.
Find feasible solution for the following system of linear inequation graphically.
3x + 4y ≥ 12, 4x + 7y ≤ 28, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
