Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An alcohol (x) gives blue colour in Victormeyer’s test and 3.7 g of X when treated with metallic sodium liberates 560 mL of hydrogen at 273 K and 1 atm pressure what will be the possible structure of X?
Options
CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3
CH3 – CH(OH) – CH3
CH3 – C(OH) (CH3)2
CH3 – CH2 – CH(OH) – CH2 – CH3
Solution
CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3
Explanation:
∴ number of moles of alcohol =
= 0.05 moles
∴ no. of moles =
molar mass =
General formula for R – OH Cn H2n+1 – OH
∴ n(12) + (2n+1) (1) + 16 + 1 = 74
14n = 74 – 18
14n = 56
∴ n =
The 2° alcohol which contains 4 carbon is CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
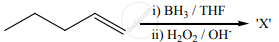
The X is
The reaction can be classified as
One mole of an organic compound (A) with the formula C3H8O reacts completely with two moles of HI to form X and Y. When Y is boiled with aqueous alkali it forms Z. Z answers the iodoform test. The compound (A) is ___________.
Identify the product(s) is/are formed when 1-methoxy propane is heated with excess HI. Name the mechanism involved in the reaction.
Can we use nucleophiles such as NH3, CH3O for the Nucleophilic substitution of alcohols?
Explain Kolbe’s reaction.
0.44 g of a monohydric alcohol, when added to methyl magnesium iodide in ether, liberates at STP 112 cm3 of methane with PCC the same alcohol form a carbonyl compound that answers the silver mirror test. Identify the compound.
Draw the major product formed when 1-ethoxyprop-1-ene is heated with one equivalent of HI
Draw the major product formed when 1-ethoxyprop-1-ene is heated with one equivalent of HI.
What will be the product (X and A) for the following reaction:
