Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer in detail:
Explain the 'Final Good Approach' to avoid double counting of goods and services in the estimation of national income.
Solution
The final goods approach: Final goods refer to those goods and services that are meant for final consumption by the consumers. For example, a packet of cotton balls at a retail shop is a final good. Such cotton is ready to be used by the consumers for various purposes without any requirement of further value addition. Similarly, a car at a showroom is a final good, ready to be driven out on the roads. Intermediate goods refer to those goods that are not readily consumed for final consumption by the consumers. These goods are used only as inputs/ raw materials in the production process. According to this method, national income is estimated by taking the market value of the final goods and services produced in an economy during an accounting year and ignoring the value of intermediate goods.
This can be understood by the following example:
| Production stages | Value of input | Value of output | Value added |
| Milk(farmer) | 0 | 400 | 400 |
| Cheese(dairy) | 400 | 800 | 400 |
| Sweets(shopkeeper) | 800 | 1200 | 400 |
| Total value | 1200 | 2400 | 1200 |
Here, we have assumed that there is only one final product (sweets) and there are three stages of production i.e. there is milk, cheese and sweets. Milk is the only input in the production of cheese and cheese is the only input in the production of sweets.
Now, the final value of sweets produced is Rs 1200. So, the national income is Rs 1200.
If we would have summed the value of output at each stage, the total value of output at each stage would have been Rs 2400. The value of cheese (800) includes the value of milk (400), as well which has already been included at the farmer’s level. Similarly, the value of sweets (1200) includes the value of cheese (800), which too has been taken care of at the dairy level. Thus, estimating the value of output at each level counts the value of a commodity twice or double times. So, the value of national income is Rs 1200.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
National income
With the increase in income, both consumption and savings increase.
Total Cost and Total Revenue.
Total Cost and Total Revenue.
Explain the various methods of measuring national income.
Explain in detail ‘saving function’ with schedule and diagram.
Find national income and private income:
(Rs crore)
(i) Wages and salaries 1,000
(ii) Net current transfer to abroad 20
(iii) Net factor income paid to abroad 10
(iv) Profit 400
(v) National debt interest 120
(vi) Social security contributions by employers 100
(vii) Current transfers from government 60
(viii) National income accruing to government 150
(ix) Rent 200
(x) Interest 300
(xi) Royalty 50
C = 100 + 0.4 Y is the Consumption Function of an economy where C is Consumption Expenditure and Y is National Income. Investment expenditure is 1.100. Calculate
(i) Equilibrium level of National Income.
(ii) Consumption expenditure at equilibrium level of national income.
Calculate National Income from the following data:
| S.No. | Particulars | Rs.in crores |
| (i) | Private final consumption expenditure | 900 |
| (ii) | Profit | 100 |
| (iii) | Government final consumption expenditure | 400 |
| (iv) | Net indirect taxes | 100 |
| (v) | Gross domestic capital formation | 250 |
| (vi) | Change in stock | 50 |
| (vii) | Net factor income from abroad | (-)40 |
| (viii) | Consumption of fixed capital | 20 |
| (ix) | Net imports | 30 |
National income is the sum of factor incomes accruing to : (Choose the correct alternative)
(a) Nationals
(b) Economic territory
(c) Residents
(d) Both residents and non-residents
Unforseen obsolescence of fixed capital assets during production is: (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Consumption of fixed capital
b. Capital loss
c. Income loss
d. None of the above
Explain the precautions that should be taken while estimating national income by expenditure method.
Calculate (a) National Income, and (b) Net National Disposable Income:
| (Rs In crores) | |
| (i) Compensation of employees | 2,000 |
| (ii) Rent | 400 |
| (iii) Profit | 900 |
| (iv) Dividend | 100 |
| (v) Interest | 500 |
| (vi) Mixed income of self- employed | 7,000 |
| (vii) Net factor income to abroad | 50 |
| (viii) Net export | 60 |
| (ix) Net indirect taxes | 300 |
| (x) Depreciation | 150 |
| (xi) Net current transfers to aboard | 30 |
Other things remaining unchanged, when in a country the price of foreign currency rises, national income is: (choose the correct alternative)
a. Likely to rise
b. Likely to fall
c. Likely to rise and fall both
d. Not affected
A government of India has recently launched 'Jan-Dhan Yojana' aimed at every household in the country to have at least one bank account. Explain how deposits made under the plan are going to affect the national income of the country.
Giving reason explain how should the following be treated in the estimation of national income:
Expenditure by a firm on payment of fees to a chartered accountant
Giving reason explain how should the following be treated in the estimation of national income:
Purchase of refrigerator by a firm for own use
Calculation National Income and Personal Disposable Income:
| (Rs crores) | ||
| 1 | Personal tax | 80 |
| 2 | Private final consumption expenditure | 600 |
| 3 | Undistributed profits | 30 |
| 4 | Private income | 650 |
| 5 | Government final consumption expenditure | 100 |
| 6 | Corporate tax | 50 |
| 7 | Net domestic fixed capital formation | 70 |
| 8 | Net indirect tax | 60 |
| 9 | Depreciation | 14 |
| 10 | Change in stocks | (-)10 |
| 11 | Net imports | 20 |
| 12 | Net factor income to abroad | 10 |
Calculation National Income and Personal Disposable Income:
| (Rs crores) | ||
| 1 | Rent | 100 |
| 2 | Net current transfers to rest of the world | 30 |
| 3 | Social security contributions by employers | 47 |
| 4 | Mixed income | 600 |
| 5 | Gross domestic capital formation | 140 |
| 6 | Royalty | 20 |
| 7 | Interest | 110 |
| 8 | Compensation of employees | 500 |
| 9 | Net domestic capital formation | 120 |
| 10 | Net factor income from abroad | (-)10 |
| 11 | Net indirect tax | 150 |
| 12 | Profit | 200 |
Giving reason explain how the following should be treated in the estimation of national income:
Payment of interest by an individual to a bank
Calculate 'Net National Product at Market Price' and 'Personal Income'.
| (Rs crore) | ||
| (i) | Transfer payments by government | 7 |
| (ii) | Government final consumption expenditure | 50 |
| (iii) | Net imports | -10 |
| (iv) | Net domestic fixed capital formation | 60 |
| (v) | Private final consumption expenditure | 300 |
| (vi) | Private income | 280 |
| (vii) | Net factor income to abroad | -5 |
| (viii) | Closing stock | 8 |
| (ix) | Opening stock | 8 |
| (x) | Depreciation | 12 |
| (xi) | Corporate tax | 60 |
| Xii | Retained earnings of corporatio | 20 |
How should the following be treated in estimating the national income of a country? You must give a reason for your answer.
Taking care of aged parents
How should the following be treated while estimating national income? You must give the reason in support of your answer.
Bonus paid to employees
Give reasons or explain the following
The propensity to save depends upon the level of income.
Give reasons or Explain the following statements
Services of housewives are excluded from national income.
In an economy, S = −100 + 0.6 Y is the saving function, where S is Saving and Y is National Income. If investment expenditure is 1,100, calculate:
(1) Equilibrium level of National Income
(2) Consumption expenditure at equilibrium level of National Income.
Distinguish between the following :
Output method and Income method of measuring national income.
Write explanatory answer:
Explain the output method of measuring national income.
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
National income is ........ concept.
Define or explain the following concept.
Disposable income.
(b) decreases
(c) becomes equal
(d) becomes zero
Define of Explain the following concept.
Net earnings from foreign trade
Write explanatory notes.
Output method of measurement of national income.
Answer in brief.
Give different definitions of National Income.
State whether the following statements are True or False with reason:
Ten years period is considered for measuring National Income.
Distinguish between Illegal income and Transfer income.
Answer the following question:
What is double counting of national income?
Answer the following question:
Explain the concept of Gross domestic product at market prices.
Answer the following question:
Explain the income method of measuring national income.
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement:
Gross National product and Gross Domestic product are same concepts.
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement:
The money value of intermediate goods is not included in the estimation of national income.
Answer in detail:
Explain the Output method of measuring National income.
Distinguish between:
Gross national product and Gross domestic product.
Distinguish between:
Gross National Product and Net National Product
Distinguish between:
National income at market prices and national income at factor cost
Write short note on:
Value added approach
Write short note on:
Personal disposable income
Write short note on:
Net national product at factor cost
Define or explain the following concept:
Final goods
Define or explain the following concept:
National income
Define or explain the following concept:
Personal income
Define or explain the following concept:
Depreciation
Give reason or explain the following statement:
National income estimates are accurate in India.
State whether the following statement is true or false.
Inclusion of value of intermediate goods leads to double counting.
State whether the following statement is true or false.
GDP includes net income from abroad.
State whether the following statement is true or false.
Financial year in India is leap year.
Match the following groups:
| Group A | Group B | ||
| 1) | Income method | a) | Personal income – direct taxes |
| 2) | Unemployment allowance | b) | Money value of goods and services |
| 3) | Disposable Income | c) | Factor cost method |
| 4) | National Income | d) | Personal income subsidy |
| 5) | NNP(MP) | e) | Transfer payment |
| f) | GNP(MP) - Depreciation | ||
| g) | Output method | ||
| h) | Transfer income | ||
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below
National income is the subject matter of _________ Economics.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below
In India, the responsibility for the calculation of national income rests with _________.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below
National income is __________ concept.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below
Paper purchased by a publisher is __________.
Distinguish between the following.
Personal income and Disposable income
Find the odd word
Concepts of national income -
Complete the following statement.
NNP is obtained by ______.
Assertion and Reasoning type question.
Assertion (A): In national income, value of only final goods and services produced in the economy are considered.
Reasoning (R): National income is always expressed in monetary terms.
Study the following table, figure, passage and answer the question given below it.
| Components of GNP for the year 2018 |
In crores |
| Consumption | 200 |
| Investment | 300 |
| Govt.Expenditure | 400 |
| Net export | - 100 |
| Net receipts | - 50 |
| Depreciation | 100 |
A. Complete the formula
GNP = C + `square` + G + (X - M) + `square` (1m)
B. Calculate Gross National Product & Net National Product from the above data. (3m)
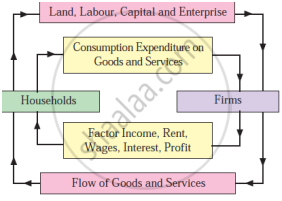
- Explain the concept of product (real flow) with the help of above diagram. (2m)
- Explain the concept of Money flow with the help of above diagram. (2m)
Net National product at factor cost is also known as
Which is the largest figure?
NNP stands for______.
When net factor income from abroad is deducted from NNP, the net value is______.
The average income of the country is______.
Write the formula for calculating GNP.
Trace the relationship between GNP and NNP.
Write a short note on per capita income.
What is the solution to the problem of double counting in the estimation of national income?
Explain the meaning of non-market activities.
Real GNP is same as ______.
Consider the following statements and identify the right ones.
- Personal income refers to the income of individuals of a country.
- The income at their disposal after paying direct taxes is called disposable income.
GNP at MP = ____________.
GDPFC = ____________.
NNPFC =
Accounting of National Income at constant prices is known as ____________.
GDP MP = Rs.1000 and subsidies = Rs.50, then GDP FC will be ______.
The market price of all final goods of a country in a year is known as:
Which one is true?
If economic subsidies are added to and Indirect taxes are substracted from the national income at market prices, then it will be equal to ______.
If for a country net factor income from abroad is negative then:
The market value of all final goods and services produced in an economy over a year is called:
Total national income divided by total population is known as:
Which of the following is not a component of domestic income?
If factor cost is greater than marker price, it means that:
Identify and explain the following concept.
Shobha collected data regarding the money value of all final goods and services produced in the country for the financial year 2019-20.
How should the following be treated in estimating National Income of a Country? Give valid reasons.
Expenditure on upgradation of fixed asset by a firm.
