Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
What is the unit of dipole moment?
Solution
- Strength of a dipole is measured in terms of a quantity called the dipole moment.
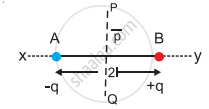
- Let q be the magnitude of each charge and `2vec"l"` be the distance from the negative charge to the positive charge. Then, the product `"q"(2vec"l")` is called the dipole moment `vec"p"`.
- Dipole moment is defined as `vec"p"="q"(2vec"l")`
- A dipole moment is a vector whose magnitude is q (2l) and the direction is from the negative to the positive charge.
- The unit of dipole moment is coulomb-meter (C m) or debye (D).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Drive the expression for electric field at a point on the equatorial line of an electric dipole.
(i)Obtain the expression for the torque `vecτ` experienced by an electric dipole of dipole moment `vecP` in a uniform electric field, `vecE` .
(ii) What will happen if the field were not uniform?
An electric dipole of length 2 cm, when placed with its axis making an angle of 60° with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque of \[8\sqrt{3}\] Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has a charge \[\pm\] 4 nC.
An electric dipole of length 1 cm, which placed with its axis making an angle of 60° with uniform electric field, experience a torque of \[6\sqrt{3} Nm\] . Calculate the potential energy of the dipole if it has charge ±2 nC.
It is said that the separation between the two charges forming an electric dipole should be small. In comparison to what should this separation be small?
A sample of HCI gas is placed in an electric field of 2.5 × 104 NC−1. The dipole moment of each HCI molecule is 3.4 × 10−30 Cm. Find the maximum torque that can act on a molecule.
Two particles A and B, of opposite charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and −2.0 × 10−6 C, are placed at a separation of 1.0 cm. Two particles A and B, of opposite charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and −2.0 × 10−6 C, are placed at a separation of 1.0 cm.
Two particles, carrying charges −q and +q and and of mass m each, are fixed at the ends of a light rod of length a to form a dipole. The rod is clamped at an end and is placed in a uniform electric field E with the axis of the dipole along the electric field. The rod is slightly tilted and then released. Neglecting gravity, find the time period of small oscillations.
Two-point charges Q1 = 400 μC and Q2 = 100 μC are kept fixed, 60 cm apart in a vacuum. Find the intensity of the electric field at the midpoint of the line joining Q1 and Q2.
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity of 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 Nm. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is ______.
A uniform electric field is prevailing in X - direction in certain region. The coordinates of points P, Q, and R are (0, 0), (2, 0) and (0, 2) respectively. Which of the following alternatives is true for the potentials at these points?
An electric dipole of moment p is placed parallel to the uniform electric field. The amount of work done in rotating the dipole by 90° is ____________.
The electric intensity due to a dipole of length 10 cm and having a charge of 500 µC, at a point on the axis at a distance 20 cm from one of the charges in air, is:
Polar molecules are the molecules ______.
A dipole is placed in an electric field as shown. In which direction will it move?
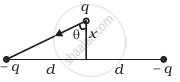
Two charges –q each are fixed separated by distance 2d. A third charge q of mass m placed at the mid-point is displaced slightly by x(x << d) perpendicular to the line joining the two fixed charged as shown in figure. Show that q will perform simple harmonic oscillation of time period.
`T = [(8pi^3 ε_0 md^3)/q^2]^(1/2)`
The electric field in a region is given by `vec"E" = 2/5"E"_0hat"i"+3/5"E"_0hat"j"` with `"E"_0 = 4.0xx10^3 "N"/"C"`. The flux of this field through a rectangular surface area 0.4 m2 parallel to the Y - Z plane is ______ Nm2C-1.
Eight dipoles of charges of magnitude e each are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be ______.
In an electric dipole, what is the locus of a point having zero potential?
