Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Briefly explain the structure of thyroid gland.
Solution
The thyroid gland is butterfly-shaped, bilobed situated below the larynx on each side of the upper trachea. The two lobes are connected by a median tissue mass called isthmus. Each lobe is made up of many lobules. The lobules consist of follicles called acini. Each acinus is lined with glandular, cuboidal, or squamous epithelial cells.
The lumen of acini is filled with colloid, a thick glycoprotein mixture consisting of thyroglobulin molecules. The thyroid gland secretes Tri-iodothyronine (T3) and tetra-iodothyronine (T4) or thyroxine hormones. These are concerned with metabolism.

Structure of Thyroid gland
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define Endocrine gland
| Hormones | Target gland |
| Melanotrophin (MSH | ______ |
A gland having endocrine as well as exocrine function is
Name the following:
The largest endocrine gland
Give the special function of the following:
Corpus luteum
Name the hormone responsible for the following function:
Ossification of bones
Name the hormone responsible for the following function:
Regulates the functioning of the male and female reproductive organs
Name the hormone responsible for the following function:
Increased reabsorption of water in the kidneys
Choose the correct answer:
Excess secretion of growth hormone causes ____________
Choose the correct answer:
Which one of the following is not an endrocine gland?
Which parts of the alimentary canal produce hormones?
Is the following gland an exocrine or an endocrine gland?
Salivary gland
Complete the table given below by filling in the blanks numbered 1 to 8.
| Gland | Hormone Secreted | Effect on Body |
| 1 | 2 | Regulates basal metabolism |
| Pancreas (β-cells) | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 | Increases heart beat |
| 7 | Thyroid stimulating hormone | 8 |
The release of progesterone in the urine is an indication of pregnancy. Explain.
Differentiate: Cretinism and Myxedema.
Give the Technical Term: What are releasing hormones?
Give the Technical Term: Name the glands which secrete the following hormone: Testosterone
Place the words at the bottom of the page next to the number that shows the location of the Endocrine Glands.

(1) ________
(2) ________
(3) ________
(4) ________
(5) ________
(6) ________
(7) ________
(8) ________
(9) ________
Pancreas Hypothalamus Pituitary Parathyroid Ovaries Adrenal Thyroid Thymus Testes
Study the diagram given below and then answer the questions that follow:
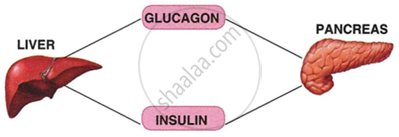 |
- Name the cells of the pancreas that produce (1) glucagon (2) insulin.
- State the main function of (1) glucagon and (2) insulin.
- Why is the pancreas referred to as an exo-endocrine gland?
- Why is insulin not given orally but is injected into the body?
- What is the technical term for the cells of the pancreas that produce endocrine hormones?
- Where in the body is the pancreas located?
Given alongside are the diagrammatic sketches of some endocrine glands. Observe the figures and answer the following questions:

(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 5.
(ii) Name the hormones secreted by (2) and (5).
(iii) Which chemicals in our body are greatly affected by hormones?
(iv) What is the chemical nature of hormones?
(v) Name the elements related to the functioning of hormones secreted by the structure (2) and (5).
The sketch below shows a certain condition in an individual:

(i) Name the condition.
(ii) What is the underlying cause of this condition?
(iii) Name two other conditions that could have resulted due to a similar cause.
(iv) Which hormone is required for iodine synthesis?
(v) Where is the thyroid gland located?
(vi) The hormone secreted by the thyroid gland is controlled from which hormone?
State the Function
Oestradiol
State the Function
Progesterone
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Leydig cells are meant for:
Which of the following hormone is not secreted under the influence of pituitary gland?
Iodised salt is essential to prevent ______.
which of the given option shows all wrong statements for thyroid gland
Statements
- It inhibits process of RBC formation
- It helps in maintenance of water and electrolytes
- Its more secretion can reduce blood pressure
- It Stimulates osteoblast
Hormones are known as chemical messenger. Justify.
Name the layers of adrenal cortex and mention their secretions.
Differentiate hyperglycemia from hypoglycemia.
Enumerate the role of kidney as an endocrine gland.
Write a detailed account of gastro intestinal tract hormones.
Given below is the figure showing the human urinary system with structures labelled A to D. Select the option which correctly identifies them and gives their function.
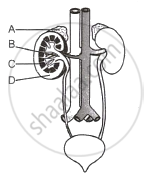
Which of the following is not an endocrine gland?
