Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
C is a point on the minor arc AB of the circle, with centre O. Given ∠ACB = p°, ∠AOB = q°.
(i) Express q in terms of p.
(ii) Calculate p if ACBO is a parallelogram.
(iii) If ACBO is a parallelogram, then find the value of q + p.
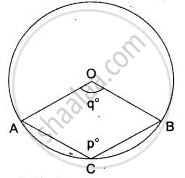
Solution
(i) Reflex ∠ AOB = 360° - q°
ACB = `1/2`reflex ∠ AOB .....(angle at the centre property)
p° = `1/2` (360° - q°)
2p° = 360° - q°
q° = 360° - 2p°
q = 360° - 2p
(ii) If ACBO is a parallelogram, then
p = q
q = 360° - 2p
p = 360° - 2p
p + 2p = 360°
p = `(360°)/3 = 120°`
(iii) If ACBO is a parallelogram, then
p = q
Also, p = 120° ....(From(ii))
p + q = p + p = 2p
p + q = 2 + 120°= 240°.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
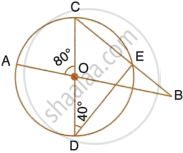
In the figure given alongside, AB and CD are straight lines through the centre O of a circle. If ∠AOC = 80° and ∠CDE = 40°, find the number of degrees in:
- ∠DCE,
- ∠ABC.
Two chords AB and CD intersect at P inside the circle. Prove that the sum of the angles subtended by the arcs AC and BD at the centre O is equal to twice the angle APC.
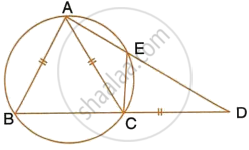
In the given figure, AB = AC = CD and ∠ADC = 38°. Calculate :
- Angle ABC
- Angle BEC
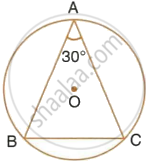
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle in which ∠BAC = 30°. Show that BC is equal to the radius of the circumcircle of the triangle ABC, whose centre is O.
The given figure shows a circle with centre O such that chord RS is parallel to chord QT, angle PRT = 20° and angle POQ = 100°. Calculate:
(iv) angle STR

In the given figure, an equilateral triangle ABC is inscribed in a circle with center O.
Find: (i) ∠BOC
(ii) ∠OBC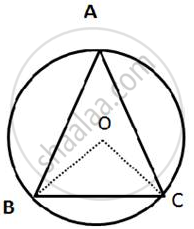
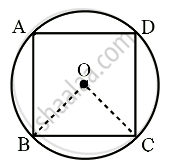
In the given figure, a square is inscribed in a circle with center O. Find:
- ∠BOC
- ∠OCB
- ∠COD
- ∠BOD
Is BD a diameter of the circle?
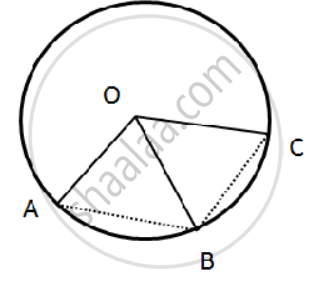
In the given figure, AB = BC = DC and ∠AOB = 50°.
(i) ∠AOC
(ii) ∠AOD
(iii) ∠BOD
(iv) ∠OAC
(v) ∠ODA
In the given figure, the lengths of arcs AB and BC are in the ratio 3:2. If ∠AOB = 96°, find:
- ∠BOC
- ∠ABC
In the given figure, AB is a side of regular pentagon and BC is a side of regular hexagon.
(i) ∠AOB
(ii) ∠BOC
(iii) ∠AOC
(iv) ∠OBA
(v) ∠OBC
(vi) ∠ABC
