Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate Ecell and ΔG for the following at 28°C :
Mg(s) + Sn2+( 0.04M ) → Mg2+( 0.06M ) + Sn(s)
E°cell = 2.23V. Is the reaction spontaneous ?
Solution
`Mg_(s) + Sn_(aq)^(2+) -> Mg_(aq)^(2+) + Sn_(s)`
`[Sn^(2+)] = 0.04M[Mg^(2+)] = 0.06M`
Q = `[Mg^(2+)]/[Sn^(2+)] = [0.06]/[0.04] = 1.5`
`E_(cell)^(°) = 2.23V`
R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
T = 28°C = 28 + 273 = 301K
n = 2
F = 96500 C/mol e-
∴ `E_(cell) = E_(cell)^(°) - [2.303 RT]/[nF] log_10 Q`
= `2.23 - [2.303 xx 8.314 xx 301]/[2 xx 96500] log_10 (1.5)`
= `2.23 - [2.303 xx 8.314 xx 301]/[2 xx 96500] xx (0.1760)`
= 2.23 - 0.005255
`E_(cell)` = -2.2247 V
ΔG = `nFE_(cell)`
ΔG = `-2 xx 96500 xx 2.2247`
ΔG = - 429367 J
∵ ΔG is negative therefore reaction is spontaneous.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of primary reference electrode.
Arrange the following reducing agents in the order of increasing strength under standard state conditions. Justify the answer
|
Element |
Al(s) |
Cu(s) |
Cl(aq) |
Ni(s) |
|
Eo |
-1.66V |
0.34V |
1.36V |
-0.26V |
Can copper sulphate solution be stored in an iron vessel? Explain.
Calculate E°cell for the following reaction at 298 K:
2Al(s) + 3Cu+2(0.01M) → 2Al+3(0.01M) + 3Cu(s)
Given: Ecell = 1.98V
Calculate emf of the following cell at 25°C:
\[\ce{Sn/Sn^2+ (0.001 M) || H+ (0.01 M) | H2_{(g)} (1 bar) | Pt_{(s)}}\]
Given: \[\ce{E^\circ(Sn^2+/sn) = -0.14 V, E^\circ H+/H2 = 0.00 V (log 10 = 1)}\]
Calculate e.m.f of the following cell at 298 K:
2Cr(s) + 3Fe2+ (0.1M) → 2Cr3+ (0.01M) + 3 Fe(s)
Given: E°(Cr3+ | Cr) = – 0.74 VE° (Fe2+ | Fe) = – 0.44 V
Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction \[\ce{Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Zn^{2+}(aq) + 2Ag(s)}\] takes place. Further show:
- Which of the electrode is negatively charged?
- The carriers of the current in the cell.
- Individual reaction at each electrode.
In the representation of the galvanic cell, the ions in the same phase are separated by a _______.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the lead storage battery.
Calculate the emf of the following cell at 25°C :
Galvanic or a voltaic cell converts the chemical energy liberated during a redox reaction to ____________.
Standard electrode potential is measured taking the concentrations of all the species involved in a half-cell is ____________.
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu indicates that:
(i) this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple.
(ii) this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2 .
(iii) Cu can displace H2 from acid.
(iv) Cu cannot displace H2 from acid.
What does the negative sign in the expression `"E"^Θ ("Zn"^(2+))//("Zn")` = − 0.76 V mean?
Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of \[\ce{Cl-}\] ions is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, why is \[\ce{Cl-}\] oxidised at anode instead of water?
Which reference electrode is used to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes?
Assertion: Cu is less reactive than hydrogen.
Reason: `E_((Cu^(2+))/(Cu))^Θ` is negative.
Consider the figure and answer the following question.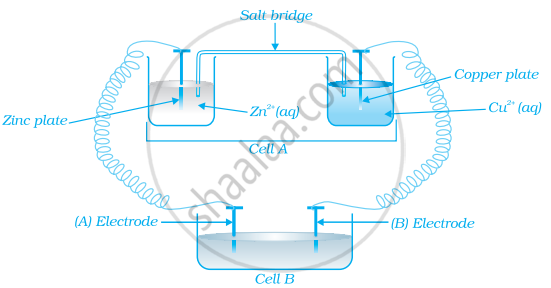
If cell ‘A’ has ECell = 0.5V and cell ‘B’ has ECell = 1.1V then what will be the reactions at anode and cathode?
Represent the cell in which the following reaction takes place.The value of E˚ for the cell is 1.260 V. What is the value of Ecell?
\[\ce{2Al (s) + 3Cd^{2+} (0.1M) -> 3Cd (s) + 2Al^{3+} (0.01M)}\]
Standard electrode potential of three metals X, Y and Z are – 1.2 V, + 0.5 V and – 3.0 V, respectively. The reducing power of these metals will be:
The potential of a hydrogen electrode at PH = 10 is
Standard reduction potentials (E°) of Cd2+, respectively which is the strongest reducing agent
The emf of a galvanic cell, with electrode potential of Zn2+ = - 0.76 V and that of Cu2+ = 0.34 V, is ______.
