Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider a wheel of a bicycle rolling on a level road at a linear speed \[\nu_0\] (see the following figure)
(a) the speed of the particle A is zero
(b) the speed of B, C and D are all equal to \[v_0\]
(c) the speed of C is 2 \[v_0\]
(d) the speed of B is greater than the speed of O.

Solution
(a) the speed of the particle A is zero
(c) the speed of C is 2 \[v_0\]
(d) the speed of B is greater than the speed of O
For pure rolling,
\[\omega r = v_0\]
Velocity of the particle at A, B, C and D will be resultant of v0 and ωr.
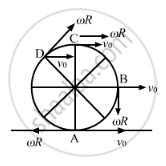
At point B,
\[v_{net} = \sqrt{{v_0}^2 + \left( \omega r \right)^2}\]
\[ v_{net} = \sqrt{{v_0}^2 + {v_0}^2}\]
\[ v_{net} = \sqrt{2} v_0\]
At point C,
\[v_{net} = v_0 + \left( \omega r \right)\]
\[ v_{net} = 2 v_0\]
At point A,
\[v_{net} = v_0 - \left( \omega r \right)\]
\[ v_{net} = 0\]
At point O,
r = 0
\[\therefore v_{net} = v_0\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A hollow sphere, a solid sphere, a disc and a ring all having same mass and radius are rolled down on an inclined plane. If no slipping takes place, which one will take the smallest time to cover a given length?
A circular disc A of radius r is made from an iron plate of thickness t and another circular disc B of radius 4r is made from an iron plate of thickness t/4. The relation between the moments of inertia IA and IB is __________ .
A thin circular ring of mass M and radius r is rotating about its axis with an angular speed ω. Two particles having mass m each are now attached at diametrically opposite points. The angular speed of the ring will become
A wheel of radius 20 cm is pushed to move it on a rough horizontal surface. If is found to move through a distance of 60 cm on the road during the time it completes one revolution about the centre. Assume that the linear and the angular accelerations are uniform. The frictional force acting on the wheel by the surface is ______________________ .
A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a disc, all having same mass and radius, are placed at the top on an incline and released. The friction coefficients between the objects and the incline are same and not sufficient to allow pure rolling. Least time will be taken in reaching the bottom by ___________ .
Three particles, each of mass 200 g, are kept at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 10 cm. Find the moment of inertial of the system about an axis joining two of the particles.

Three particles, each of mass 200 g, are kept at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 10 cm. Find the moment of inertial of the system about an axis passing through one of the particles and perpendicular to the plane of the particles.

Particles of masses 1 g, 2 g, 3 g, .........., 100 g are kept at the marks 1 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm, ..........., 100 cm respectively on a metre scale. Find the moment of inertia of the system of particles about a perpendicular bisector of the metre scale.
The moment of inertia of a uniform rod of mass 0⋅50 kg and length 1 m is 0⋅10 kg-m2about a line perpendicular to the rod. Find the distance of this line from the middle point of the rod.
The radius of gyration of a uniform disc about a line perpendicular to the disc equals its radius. Find the distance of the line from the centre.
Find the moment of inertia of a uniform square plate of mass m and edge a about one of its diagonals.
Because of the friction between the water in oceans with the earth's surface the rotational kinetic energy of the earth is continuously decreasing. If the earth's angular speed decreases by 0⋅0016 rad/day in 100 years find the average torque of the friction on the earth. Radius of the earth is 6400 km and its mass is 6⋅0 × 1024 kg.
Suppose the rod in the previous problem has a mass of 1 kg distributed uniformly over its length.
(a) Find the initial angular acceleration of the rod.
(b) Find the tension in the supports to the blocks of mass 2 kg and 5 kg.
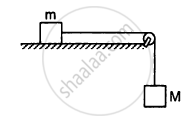
The following figure shows two blocks of mass m and M connected by a string passing over a pulley. The horizontal table over which the mass m slides is smooth. The pulley has a radius r and moment of inertia I about its axis and it can freely rotate about this axis. Find the acceleration of the mass M assuming that the string does not slip on the pulley.
A metre stick weighing 240 g is pivoted at its upper end in such a way that it can freely rotate in a vertical place through this end (see the following figure). A particle of mass 100 g is attached to the upper end of the stick through a light string of length 1 m. Initially, the rod is kept vertical and the string horizontal when the system is released from rest. The particle collides with the lower end of the stick and sticks there. Find the maximum angle through which the stick will rise.
A sphere of mass m rolls on a plane surface. Find its kinetic energy at an instant when its centre moves with speed \[\nu.\]
A small spherical ball is released from a point at a height h on a rough track shown in the following figure. Assuming that it does not slip anywhere, find its linear speed when it rolls on the horizontal part of the track.

