Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The density of a rod gradually decreases from one end to the other. It is pivoted at an end so that it can move about a vertical axis though the pivot. A horizontal force F is applied on the free end in a direction perpendicular to the rod. The quantities, that do not depend on which end of the rod is pivoted, are ________________ .
Options
angular acceleration
angular velocity when the rod completes one rotation
angular momentum when the rod completes one rotation
torque of the applied force
Solution
torque of the applied force
The torque of the applied force does not depend on the density of a rod. It depend on the distance between the pivot and the point where F is applied. So, it does not depend on which end of the rod is pivoted.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the components along the x, y, z axes of the angular momentum l of a particle, whose position vector is r with components x, y, z and momentum is p with components px, py and 'p_z`. Show that if the particle moves only in the x-y plane the angular momentum has only a z-component.
The torque of the weight of any body about any vertical axis is zero. If it always correct?
If several forces act on a particle, the total torque on the particle may be obtained by first finding the resultant force and then taking torque of this resultant. Prove this. Is this result valid for the forces acting on different particles of a body in such a way that their lines of action intersect at a common point?
If the resultant torque of all the forces acting on a body is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will be zero about any other point?
A simple pendulum of length l is pulled aside to make an angle θ with the vertical. Find the magnitude of the torque of the weight ω of the bob about the point of suspension. When is the torque zero?
When a force of 6⋅0 N is exerted at 30° to a wrench at a distance of 8 cm from the nut it is just able to loosen the nut. What force F would be sufficient to loosen it if it acts perpendicularly to the wrench at 16 cm from the nut?

Calculate the total torque acting on the body shown in the following figure about the point O.

A 6⋅5 m long ladder rests against a vertical wall reaching a height of 6⋅0 m. A 60 kg man stands half way up the ladder.
- Find the torque of the force exerted by the man on the ladder about the upper end of the ladder.
- Assuming the weight of the ladder to be negligible as compared to the man and assuming the wall to be smooth, find the force exerted by the ground on the ladder.
A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
A particle of mass m is moving in yz-plane with a uniform velocity v with its trajectory running parallel to + ve y-axis and intersecting z-axis at z = a (Figure). The change in its angular momentum about the origin as it bounces elastically from a wall at y = constant is ______.
Figure shows two identical particles 1 and 2, each of mass m, moving in opposite directions with same speed v along parallel lines. At a particular instant, r1 and r2 are their respective position vectors drawn from point A which is in the plane of the parallel lines. Choose the correct options:
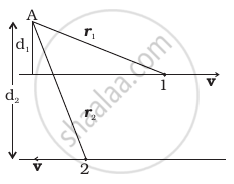
- Angular momentum l1 of particle 1 about A is l1 = mvd1
- Angular momentum l2 of particle 2 about A is l2 = mvr2
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv(r1 + r2)
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv (d2 − d1)
⊗ represents a unit vector coming out of the page.
⊗ represents a unit vector going into the page.
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
A uniform cube of mass m and side a is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. A vertical force F is applied to the edge as shown in figure. Match the following (most appropriate choice):
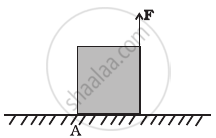
| (a) mg/4 < F < mg/2 | (i) Cube will move up. |
| (b) F > mg/2 | (ii) Cube will not exhibit motion. |
| (c) F > mg | (iii) Cube will begin to rotate and slip at A. |
| (d) F = mg/4 | (iv) Normal reaction effectively at a/3 from A, no motion. |
The position vector of 1 kg object is `vecr = (3hati - hatj)` m and its velocity `vecv = (3hati + hatk)` ms-1. The magnitude of its angular momentum is `sqrtx` Nm where x is ______.
The magnitude of the torque on a particle of mass 1 kg is 2.5 Nm about the origin. If the force acting on it is 1 N, and the distance of the particle from the origin is 5 m, the angle between the force and the position vector is (in radians) ______.
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased while keeping the mass the same, which one of the following will not be affected?
