Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The torque of the weight of any body about any vertical axis is zero. If it always correct?
Solution
No, its not always correct.

Explanation: If the centre of mass of the body is not on the same vertical line as the normal reaction R of the body, a net torque acts on the body about its vertical axis. In fig. 1, R and CM lies in the same vertical line. Thus, there is no torque about any vertical axis
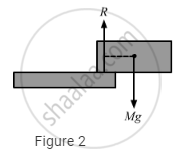
But in fig. 2, as R and CM do not lie along the same vertical line, there exists a torque about the vertical axis.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the components along the x, y, z axes of the angular momentum l of a particle, whose position vector is r with components x, y, z and momentum is p with components px, py and 'p_z`. Show that if the particle moves only in the x-y plane the angular momentum has only a z-component.
A rectangular brick is kept on a table with a part of its length projecting out. It remains at rest if the length projected is slightly less than half the total length but it falls down if the length projected is slightly more than half the total length. Give reason.
A ladder is resting with one end on a vertical wall and the other end on a horizontal floor. If it more likely to slip when a man stands near the bottom or near the top?
Equal torques act on the disc A and B of the previous problem, initially both being at rest. At a later instant, the linear speeds of a point on the rim of A and another point on the rim of B are \[\nu_A\] and \[\nu_B\] respectively. We have
When a force of 6⋅0 N is exerted at 30° to a wrench at a distance of 8 cm from the nut it is just able to loosen the nut. What force F would be sufficient to loosen it if it acts perpendicularly to the wrench at 16 cm from the nut?

A cubical block of mass m and edge a slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination θ with a uniform speed. Find the torque of the normal force acting on the block about its centre.
A flywheel of moment of inertia 5⋅0 kg-m2 is rotated at a speed of 60 rad/s. Because of the friction at the axle it comes to rest in 5⋅0 minutes. Find (a) the average torque of the friction (b) the total work done by the friction and (c) the angular momentum of the wheel 1 minute before it stops rotating.
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
Two discs of the same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through centre and perpendicular to the plane of the disc with angular velocities ω1 and ω2. They are brought in to contact face to face coinciding with the axis of rotation. The expression for loss of energy during this process is, ______
What are the conditions in which force can not produce torque?
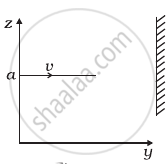
A particle of mass m is moving in yz-plane with a uniform velocity v with its trajectory running parallel to + ve y-axis and intersecting z-axis at z = a (Figure). The change in its angular momentum about the origin as it bounces elastically from a wall at y = constant is ______.
Choose the correct alternatives:
- For a general rotational motion, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω need not be parallel.
- For a rotational motion about a fixed axis, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion , momentum p and velocity v are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion, acceleration a and velocity v are always parallel.
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
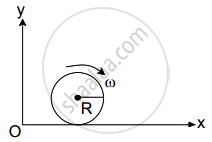
A spherical shell of 1 kg mass and radius R is rolling with angular speed ω on horizontal plane (as shown in figure). The magnitude of angular momentum of the shell about the origin O is `a/3 R^2` ω. The value of a will be:
A particle of mass 'm' is moving in time 't' on a trajectory given by
`vecr = 10alphat^2hati + 5beta(t - 5)hatj`
Where α and β are dimensional constants.
The angular momentum of the particle becomes the same as it was for t = 0 at time t = ______ seconds.
Angular momentum of a single particle moving with constant speed along the circular path ______.
The magnitude of the torque on a particle of mass 1 kg is 2.5 Nm about the origin. If the force acting on it is 1 N, and the distance of the particle from the origin is 5 m, the angle between the force and the position vector is (in radians) ______.
