Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define Electric power
Solution 1
Electric power is the rate of doing work or it is the work done in 1 second.
Electric Power(P) = `"Electric work (w)"/"time(t)"`
The S. I. unit of power is ‘Watt’.
If a current of 1 ampere flows through a metallic conductor at a potential difference of 1 volt, the power is said to be 1 watt.
or 1 Watt = 1 Volt × 1 Ampere.
Solution 2
Electric power (P) is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred or consumed in an electrical circuit. It can be represented by the formula
P = IV
Where:
- P is the electric power in watts (W),
- I is current in amperes (A), and
- V is the potential difference (voltage) in volts (V).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is consumed using different electrical appliances, for which electricity bills are paid?
1 calorie = _________ joule.
State two factors on which the electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance depends.
Which uses more energy : a 250 W TV set in 1 hour or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes?
Why is an electric light bulb not filled with air? Explain why argon or nitrogen is filled in an electric bulb.
An electric iron is rated at 750 W, 230 V. Calculate the electrical energy consumed by the iron in 16 hours .
An electrical appliance having a resistance of 200Ω is operated at 200 V. Calculate the energy consumed by the appliance in 5 minutes (i) in joules (ii) in kWh.
An immersion heater rated 1000 W, 220 V is used to heat 0.01 m3 of water. Assuming that the power is supplied at 220 V and 60% of the power supplied is used to heat the water, how long will it take to increase the temperature of the water from 15°C to 40°C?
A simple electric circuit has 24 V battery and a resistor of 60 Ω. What will be the current in the circuit? The resistance of the connecting wires is negligible.
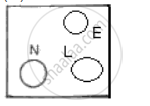
The diagram 31 shows a 3 terminal plug socket.
(i) What is the purpose of the terminal E?
(ii) To which part of the appliance is the terminal E connected?
(iii) To which wire L or N, is the fuse connected and why?
An electric bulb of resistance 500 Ω draws current 0.4 A from the source. Calculate:
- the power of bulb and
- the potential difference at its end.
An electric current is passed through a metallic wire. The wire gets heated up. Give the reason. Is it possible to melt the wire by passing a heavy current?
A device is used to transform 12 V a.c. to 200 V a.c. What is the name of this device? Name the principle on which it works.
Which material is the calorimeter commonly made of? Give one reason for using this material.
What do you understand by ‘earthing’? What are the advantages of earthing in a household electric circuit? Explain, how it is done?
State the reason why, in a three pin plug, the earth pin is longer and thicker than the other two.
A family uses a light bulb of 100W, a fan of 100W, and a heater of 1000W, each for 8 hours a day. If the cost of electricity is Rs. 2 per unit, what is the expenditure to the family per day, on electricity?
An electric lamp A of 40 W and another electric lamp B of 100 W are connected to 220 V supply. Calculate the ratio of their filament resistances?
Two bulbs are rated: bulb A 100W, 120 V bulb B 10W, 120 V. If both are connected across a 120V supply, which bulb will consume more energy, When in series? Also calculate the current through each bulb in above cases.
A. bulb is rated at 100W, 250V and another one at 60W, 250V. What is the current flowing in the circuit if the two bulbs are put in series across a 220 V mains supply?
Electric power is inversely proportional to ____________.
In the given figure, the emf of the cell is 2.2 V, and if internal resistance is 0.6 Ω. Calculate the power dissipated in the whole circuit.

