Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
'EcoRI' has played a very significant role in rDNA technology.
- Explain the convention for naming EcoRI.
- Write the recognition site and the cleavage sites of this restriction endonuclease.
Solution
(I) Restriction endonucleases are named as follows:
1st alphabet represents the genus of the organism from which the enzyme is isolated.
2nd and 3rd alphabet represent the species of the organism.
4th alphabet represents the strain.
The Roman number represents the order of isolation or discovery of the enzyme.
EcoRI comes from the Escherichia coli RYB strain.
In EcoRI, 'E' comes from the genus 'Escherichia' and 'co' comes from the species name 'Coli'.
The letter 'R' is derived from the name of the strain RYB.
Roman numbers following the names indicate the order in which the enzymes were isolated from that strain of bacteria.
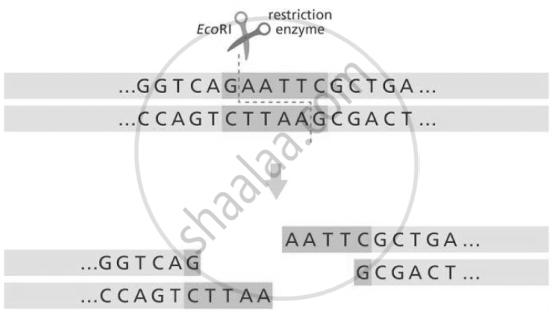
(II) The recognition sequence where EcoRI cleaves the DNA molecule is G/AATTC. Such sequences have a complementary sequence, CTTAA/G, which is known as a palindromic sequence.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain with the help of a suitable example the naming of a restriction endonuclease.
How does a restriction nuclease function? Explain
Distinguish between exonuclease and endonuclease
Restriction enzymes ______.
DNA fragments separate according to size through?
A specific recognition sequence identified by endonucleases to make cuts at specific positions within the DNA is ______
Which of the following bacteria is not a source of restriction endonuclease?
A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in an agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed. What could be the reason?
Given below is the stepwise schematic representation of the process of electrophoresis. Identify the 'alphabets' representing
- Anode end
- smallest/lightest DNA strand in the matrix
- Agarose gel

How are DNA fragments visualised once they are separated by gel electrophoresis?
