Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the anomalous behaviour of chromium.
Solution
- Chromium (Cr) has atomic number 24.
- Its expected electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d4.
- The 3d orbital is less stable as it is not half-filled.
- Due to inter electronic repulsion forces, one 4s electron enters into 3d orbital. This makes 4s and 3d orbitals half-filled which gives extra stability and the electronic configuration of Cr becomes 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Define the term Electronic configuration
Write orbital notations for the electron in orbitals with the following quantum numbers.
n = 3, l = 2
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Oxygen (Z = 8)
Draw shapes of 2s orbitals.
Draw shapes of 2p orbitals.
Explain in brief, the significance of the azimuthal quantum number.
The electronic configuration of oxygen is written as 1s2 2s2 \[\ce{2p^2_{{x}}}\] \[\ce{2p^1_{{y}}}\] \[\ce{2p^1_{{z}}}\] and not as 1s2 2s2 \[\ce{2p^2_{{x}}}\], \[\ce{2p^2_{{y}}}\] \[\ce{2p^0_{{z}}}\], Explain.
Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in \[\ce{Si}\] (Z = 14).
The designation of a subshell with n = 6 and l = 2 is ____________.
How many electrons in 19K have n = 3, l = 1?
Which of the following has a greater number of electrons than neutrons?
(Mass number of Mg, C, O and Na is 24, 12, 16 and 23 respectively).
Which of the following options does not represent ground state electronic configuration of an atom?
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
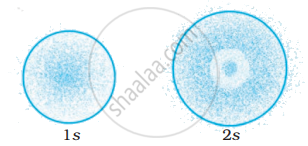
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region.
On the basis of above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect?
Which of the following properties of atom could be explained correctly by Thomson Model of atom?
Orbital angular momentum depends on ______.
Out of the following pairs of electrons, identify the pairs of electrons present in degenerate orbitals:
| (i) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -1, m_s = - 1/2` | |
| (ii) | (a) `n = 3, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iii) | (a) `n = 4, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iv) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = + 1/2` |
In which of the following pairs, the ions are iso-electronic?
(i) \[\ce{Na^{+}, Mg^{2+}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Al3^{+}, O-}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Na+ , O2-}\]
(iv) \[\ce{N3-, Cl-}\]
Nickel atom can lose two electrons to form \[\ce{Ni^{2+}}\] ion. The atomic number of nickel is 28. From which orbital will nickel lose two electrons.
Which of the following orbitals are degenerate?
3dxy, 4dxy 3dz2, 3dyz, 4dyz, 4dz2
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy.
4s, 3s, 3p, 4d
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, solve the questions given below:
Which of the following orbitals has the lowest energy?
5p, 5d, 5f, 6s, 6p
Match the following species with their corresponding ground state electronic configuration.
| Atom / Ion | Electronic configuration |
| (i) \[\ce{Cu}\] | (a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 |
| (ii) \[\ce{Cu^{2+}}\] | (b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 |
| (iii) \[\ce{Zn^{2+}}\] | (c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1 |
| (iv) \[\ce{Cr^{3+}}\] | (d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 |
| (e) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 |
Match the quantum numbers with the information provided by these.
| Quantum number | Information provided |
| (i) Principal quantum number | (a) orientation of the orbital |
| (ii) Azimuthal quantum number | (b) energy and size of orbital |
| (iii) Magnetic quantum number | (c) spin of electron |
| (iv) Spin quantum number | (d) shape of the orbital |
Match species given in Column I with the electronic configuration given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{Cr}\] | (a) [Ar]3d84s0 |
| (ii) \[\ce{Fe^{2+}}\] | (b) [Ar]3d104s1 |
| (iii) \[\ce{Ni^{2+}}\] | (c) [Ar]3d64s0 |
| (iv) \[\ce{Cu}\] | (d) [Ar] 3d54s1 |
| (e) [Ar]3d64s2 |
Choose the INCORRECT statement
Which of the following is not the permissible arrangement of electrons in an atom?
Which of the following element do not follow Aufbau principle?
