Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the determination of unknown resistance using meter bridge.
Solution
The meter bridge is another form of Wheatstone’s bridge. It consists of a uniform manganin wire AB of one meter length. This wire is stretched along a meter scale on a wooden board between two copper strips C and D. Between these two copper strips another copper strip E is mounted to enclose two gaps G1 and G2 An unknown resistance P is connected in G1 and a standard resistance Q is connected in G2.
A jockey (conducting wire) is connected to the terminal E on the central copper strip through a galvanometer (G) and a high resistance (HR). The exact position of jockey on the wire can be read on the scale. A Lechlanche cell and a key (K) are connected across the ends of the bridge wire.

Meter bridge
The position of the jockey on the wire is adjusted so that the galvanometer shows zero deflection. Let the point be J. The lengths AJ and JB of the bridge wire now replace the resistance R and S of the Wheatstone’s bridge. Then
`"P"/"Q" = "R"/"S" = ("R"' *"AJ")/("R"'*"JB")` ....(1)
where R’ is the resistance per unit length of wire
`"P"/"Q" = "AJ"/"JB" = l_1/l_2` ....(2)
P = Q `l_1/l_2` ....(3)
The bridge wire is soldered at the ends of the copper strips. Due to imperfect contact, some resistance might be introduced at the contact. These are called end resistances. This error can be eliminated, if another set of readings are taken with P and Q interchanged and the average value of P is found.
To find the specific resistance of the material of the wire in the coil P, the radius r and length l of the wire is measured. The specific resistance or resistivity r can be calculated using the relation.
Resistance = ρ - `l/"A"`
By rearranging the above equation, we get
ρ = Resistance `xx "A"/l`
If P is the unknown resistance, equation (4) becomes
ρ = P`(pi"r"^2)/l`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
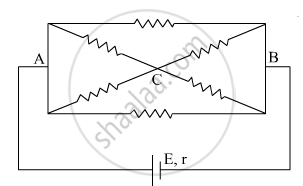
The current is drawn from a cell of emf E and internal resistance r connected to the network of resistors each of resistance r as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for
- the current draw from the cell and
- the power consumed in the network.
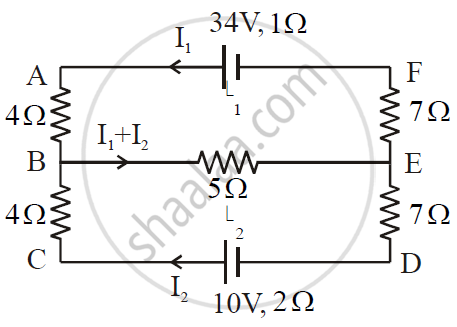
ε1 and ε2 are two batteries having emf of 34V and 10V respectively and internal resistance of 1Ω and 2Ω respectively. They are connected as shown in the figure below. Using Kirchhoff’s Laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.
State Kirchhoff's rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff's rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.
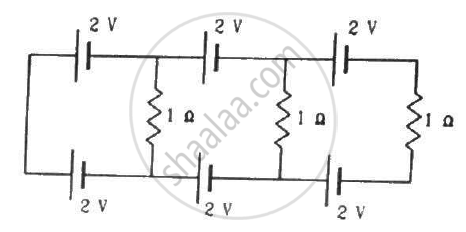
Find the circuit in the three resistors shown in the figure.
Twelve wires, each of equal resistance r, are joined to form a cube, as shown in the figure. Find the equivalent resistance between the diagonally-opposite points a and f.

On which conservation principle is Kirchoff's Second Law of electrical networks based?
Lightning is a very good example of a natural current. In typical lightning, there is 109 J energy transfer across the potential difference of 5 × 107 V during a time interval of 0.2 s. Using this information, estimate the following quantities:
- the total amount of charge transferred between cloud and ground
- the current in the lightning bolt
- the power delivered in 0.2 s.

Kirchhoff’s second law is a consequence of law of conservation of ______.
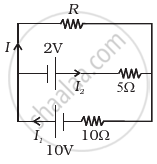
Two cells of voltage 10V and 2V and internal resistances 10Ω and 5Ω respectively, are connected in parallel with the positive end of 10V battery connected to negative pole of 2V battery (Figure). Find the effective voltage and effective resistance of the combination.
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in the analysis of electric circuits and explain them.
