Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain two types of diffraction of light.
Solution
The diffraction phenomenon is classified into two types:
1. Fraunhofer diffraction: The source of light and the screen on which the diffraction pattern is obtained are effectively at infinite distance from the diffracting system. In this case, we consider plane wavefront. The diffraction pattern is obtained by using a convex lens.
2. Fresnel diffraction: The source of light and the screen are kept at finite distance from the diffracting system. In this case, we consider a cylindrical or spherical wavefront.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is 'diffraction of light'
In a single slit diffraction pattern, the distance between first minima on the right and first minima on the left of central maximum is 4 mm. The screen on which the pattern is displaced, is 2m from the slit and wavelength of light used is 6000Å. Calculate width of the slit and width of the central maximum.
In the diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width 'd' with incident light of wavelength 'λ', at an angle of diffraction θ. the condition for first minimum is ....
(a)`lambda sin theta =d`
(b) `d costheta =lambda`
(c)`d sintheta=lambda`
(d) `lambda cos theta=d`
Explain why the maxima at `theta=(n+1/2)lambda/a` become weaker and weaker with increasing n
Two wavelengths of sodium light of 590 nm and 596 nm are used in turn to study the diffraction taking place at a single slit of aperture 2 × 10−6 m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1·5 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
In Fraunhofer diffraction, how is the angular width of the central bright fringe affected when slit separation is increased?
Draw the intensity distribution for the diffraction bands produced due to single slit ?
Two wavelengths of sodium light 590 nm and 596 nm are used, in turn to study the diffraction taking place at a single slit of aperture 2 × 10−4m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.5 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of the first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
Two wavelengths of sodium light 590 nm and 596 nm are used, in turn, to study the diffraction taking place due to a single slit of aperture 1 × 10−4 m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.8 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of the first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
In a single slit diffraction experiment, how does the angular width of the central maxima change when:
- screen is moved away from the plane of the slit?
- width of the slit is increased?
- light of larger wavelength is used?
Wavelength of light of frequency 100 Hz is
The penetration of light into the region of geomaterial shadow is called.
Diffraction effects are easy to notice in the case of sound waves than in case of light waves because
Direction of the first secondary maximum in the Fraunhoffer diffraction pattern at a single slit is given by (a is the width of the slit):
Which of the following device is used to study the spectra of light?
Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of the hole is increased ______.
- the size decreases.
- the intensity increases.
- the size increases.
- the intensity decreases.
A polariod (I) is placed in front of a monochromatic source. Another polatiod (II) is placed in front of this polaroid (I) and rotated till no light passes. A third polaroid (III) is now placed in between (I) and (II). In this case, will light emerge from (II). Explain.
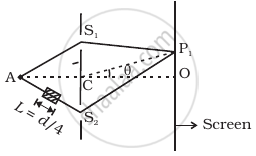
AC = CO = D, S1C = S2C = d << D
A small transparent slab containing material of µ = 1.5 is placed along AS2 (Figure). What will be the distance from O of the principal maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab?
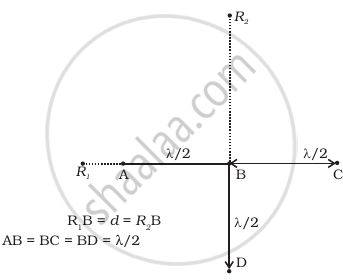
Four identical monochromatic sources A, B, C, D as shown in the (Figure) produce waves of the same wavelength λ and are coherent. Two receiver R1 and R2 are at great but equal distances from B.
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when B is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when D is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources B or D has been turned off?
Write two points of difference between an interference pattern and a diffraction pattern.
In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit, how will the angular width of the central maximum change, if the screen is moved closer to the slit?
Justify your answer.
