Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the vector and the Cartesian equations of the lines that pass through the origin and (5, −2, 3).
Solution
The required line passes through the origin. Therefore, its position vector is given by,
`veca = vec0` ...(1)
The direction ratios of the line through origin and (5, −2, 3) are
(5 − 0) = 5, (−2 − 0) = −2, (3 − 0) = 3
The line is parallel to the vector given by the equation, `vecb = 5hati - 2hatj + 3hatk`
The equation of the line in vector form through a point with position vector `veca` and parallel to `vecb` is, `vecr = veca + lambdavecb`, `lambda in R`
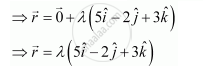
The equation of the line through the point (x1, y1, z1) and direction ratios a, b, c is given by `(x-x_1)/x = (y-y_1)/b = (z-z_1)/c`
Therefore, the equation of the required line in the Cartesian form is

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The Cartestation equation of line is `(x-6)/2=(y+4)/7=(z-5)/3` find its vector equation.
If the Cartesian equations of a line are ` (3-x)/5=(y+4)/7=(2z-6)/4` , write the vector equation for the line.
The Cartesian equation of a line is `(x-5)/3 = (y+4)/7 = (z-6)/2` Write its vector form.
Find the vector and the Cartesian equations of the line that passes through the points (3, −2, −5), (3, −2, 6).
Find the vector and Cartesian equations of a line passing through (1, 2, –4) and perpendicular to the two lines `(x - 8)/3 = (y + 19)/(-16) = (z - 10)/7` and `(x - 15)/3 = (y - 29)/8 = (z - 5)/(-5)`
Find in vector form as well as in cartesian form, the equation of the line passing through the points A (1, 2, −1) and B (2, 1, 1).
The cartesian equations of a line are x = ay + b, z = cy + d. Find its direction ratios and reduce it to vector form.
Show that the three lines with direction cosines \[\frac{12}{13}, \frac{- 3}{13}, \frac{- 4}{13}; \frac{4}{13}, \frac{12}{13}, \frac{3}{13}; \frac{3}{13}, \frac{- 4}{13}, \frac{12}{13}\] are mutually perpendicular.
Find the angle between the following pair of line:
\[\overrightarrow{r} = \lambda\left( \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} \right) \text{ and } \overrightarrow{r} = 2 \hat{j} + \mu\left\{ \left( \sqrt{3} - 1 \right) \hat{i} - \left( \sqrt{3} + 1 \right) \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k} \right\}\]
Find the angle between the pairs of lines with direction ratios proportional to 5, −12, 13 and −3, 4, 5
Find the equation of the line passing through the point (1, 2, −4) and parallel to the line \[\frac{x - 3}{4} = \frac{y - 5}{2} = \frac{z + 1}{3} .\]
Find the equations of the line passing through the point (−1, 2, 1) and parallel to the line \[\frac{2x - 1}{4} = \frac{3y + 5}{2} = \frac{2 - z}{3} .\]
Show that the lines \[\frac{x - 5}{7} = \frac{y + 2}{- 5} = \frac{z}{1} \text{ and } \frac{x}{1} = \frac{y}{2} = \frac{z}{3}\] are perpendicular to each other.
If the lines \[\frac{x - 1}{- 3} = \frac{y - 2}{2 \lambda} = \frac{z - 3}{2} \text{ and } \frac{x - 1}{3\lambda} = \frac{y - 1}{1} = \frac{z - 6}{- 5}\] are perpendicular, find the value of λ.
If the coordinates of the points A, B, C, D be (1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 7), (−4, 3, −6) and (2, 9, 2) respectively, then find the angle between the lines AB and CD.
Show that the lines \[\frac{x - 1}{3} = \frac{y + 1}{2} = \frac{z - 1}{5} \text{ and } \frac{x + 2}{4} = \frac{y - 1}{3} = \frac{z + 1}{- 2}\] do not intersect.
Determine whether the following pair of lines intersect or not:
\[\frac{x - 1}{2} = \frac{y + 1}{3} = z \text{ and } \frac{x + 1}{5} = \frac{y - 2}{1}; z = 2\]
Find the equation of the perpendicular drawn from the point P (2, 4, −1) to the line \[\frac{x + 5}{1} = \frac{y + 3}{4} = \frac{z - 6}{- 9} .\] Also, write down the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from P.
Find the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the point \[\hat{i} + 6 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} \] to the line \[\overrightarrow{r} = \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} + \lambda\left( \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} \right) .\] Also, find the length of the perpendicular
Find the coordinates of the foot of perpendicular drawn from the point A(1, 8, 4) to the line joining the points B(0, −1, 3) and C(2, −3, −1).
Find the shortest distance between the following pairs of lines whose cartesian equations are : \[\frac{x - 1}{- 1} = \frac{y + 2}{1} = \frac{z - 3}{- 2} \text{ and } \frac{x - 1}{1} = \frac{y + 1}{2} = \frac{z + 1}{- 2}\]
Find the shortest distance between the lines \[\overrightarrow{r} = 6 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} + \lambda\left( \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} \right) \text{ and } \overrightarrow{r} = - 4 \hat{i} - \hat{k} + \mu\left( 3 \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} - 2 \hat{k} \right)\]
Find the distance between the lines l1 and l2 given by \[\overrightarrow{r} = \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k} + \lambda\left( 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} + 6 \hat{k} \right) \text{ and } , \overrightarrow{r} = 3 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 5 \hat{k} + \mu\left( 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} + 6 \hat{k} \right)\]
Write the vector equation of a line passing through a point having position vector \[\overrightarrow{\alpha}\] and parallel to vector \[\overrightarrow{\beta}\] .
Write the direction cosines of the line whose cartesian equations are 2x = 3y = −z.
Write the angle between the lines 2x = 3y = −z and 6x = −y = −4z.
Find the Cartesian equations of the line which passes through the point (−2, 4 , −5) and is parallel to the line \[\frac{x + 3}{3} = \frac{4 - y}{5} = \frac{z + 8}{6} .\]
Find the angle between the lines
\[\vec{r} = \left( 2 \hat{i} - 5 \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right) + \lambda\left( 3 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 6 \hat{k} \right)\] and \[\vec{r} = 7 \hat{i} - 6 \hat{k} + \mu\left( \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} \right)\]
Find the angle between the lines 2x=3y=-z and 6x =-y=-4z.
The angle between the straight lines \[\frac{x + 1}{2} = \frac{y - 2}{5} = \frac{z + 3}{4} and \frac{x - 1}{1} = \frac{y + 2}{2} = \frac{z - 3}{- 3}\] is
If a line makes angles α, β and γ with the axes respectively, then cos 2 α + cos 2 β + cos 2 γ =
The projections of a line segment on X, Y and Z axes are 12, 4 and 3 respectively. The length and direction cosines of the line segment are
The straight line \[\frac{x - 3}{3} = \frac{y - 2}{1} = \frac{z - 1}{0}\] is
Find the value of λ, so that the lines `(1-"x")/(3) = (7"y" -14)/(λ) = (z -3)/(2) and (7 -7"x")/(3λ) = ("y" - 5)/(1) = (6 -z)/(5)` are at right angles. Also, find whether the lines are intersecting or not.
The equation 4x2 + 4xy + y2 = 0 represents two ______
The equation of line passing through (3, -1, 2) and perpendicular to the lines `overline("r")=(hat"i"+hat"j"-hat"k")+lambda(2hat"i"-2hat"j"+hat"k")` and `overline("r")=(2hat"i"+hat"j"-3hat"k")+mu(hat"i"-2hat"j"+2hat"k")` is ______.
