Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give reasons:
Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes.
Solution
- The low reactivity of aryl halides is due to resonance effect and sp2 hybrid state of carbon to which halogen atom is attached.
- In aryl halides, one of the lone pairs of electrons on halogen atom is in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring. Due to resonance, the C–X bond acquires partial double bond character. Thus, the C–X bond in haloarenes is stronger and shorter than haloalkanes. Hence, it is difficult to break C–X bond in haloarenes. (e.g. C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is 169 pm as compared to C–Cl bond length in alkyl chloride which is 178 pm).
Therefore, haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH3 ->[Red P/Br2] A ->[Ag2O/H2O]B}\\|\phantom{.........................}\\
\ce{OH\phantom{.......................}}\end{array}\]
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
Bromoethane to ethoxyethane
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
1-Chloropropane to 1-nitropropane
Convert the following:
Benzyl alcohol to benzyl cyanide
Convert the following:
2-Chloropropane to propan-1-ol
HCl is added to a hydrocarbon ‘A’ \[\ce{(C4H8)}\] to give a compound ‘B’ which on hydrolysis with aqueous alkali forms tertiary alcohol ‘C’ \[\ce{(C4H10O)}\]. Identify ‘A’ ,‘B’ and ‘C’.
Complete the following reaction sequence by writing the structural formulae of the organic compound 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
\[\ce{2-Bromobutane->[Alc.KOH]A->[][Br2]B->[][NaNH2]C}\]
Observe the following and answer the question given below.

Can it react by SN1 mechanism? Justify your answer.
Explain. Aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Explain primary benzylic halide shows higher reactivity by SN1 mechanism than other primary alkyl halide.
Explain aqueous alkaline hydrolysis of tert. butyl bromide.
Which of the following is a primary halide?
The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO2 with F2 to form NO2F:
\[\ce{NO2_{(g)} + F2_{(g)} -> NO2F_{(g)} + F_{(g)} (slow)}\]
\[\ce{F_{(g)} + NO2_{(g)} -> NO2F_{(g)} (fast)}\]
The order of the reaction with respect to NO2(g)
Which one is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction?
What type of hybridisation is present in carbocation formed during the alkaline hydrolysis of 1- bromo-1- phenyl ethane?
\[\ce{C6H5CH2Cl + KCN(alc) -> X + Y}\]
Compounds X and Y are ____________.
Identify major product 'B' in the following reaction.
\[\ce{But-1-ene ->[HBr][Peroxide] A ->[AgCN][\Delta] B}\]
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is ______.
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3 - c - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether]}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reactions giving a major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}
\end{array}\]
Observe the following and answer the questions given below:
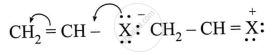
Name the type of halogen derivative.
Define and explain the SN1 mechanism with a suitable example.
Identify the chiral molecule from the following.
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...............}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether]A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
\end{array}\]
