Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How much work has to be done in assembling three charged particles at the vertices of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure?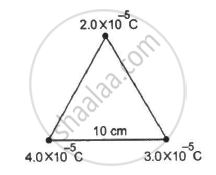
Solution
Let
Side of the equilateral triangle = l
As
Work done in assembling the charges = Net potential energy of the system
\[\Rightarrow W = U_{12} + U_{13} + U_{23} \]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\left( \frac{q_1 q_2}{l} + \frac{q_1 q_3}{l} + \frac{q_2 q_3}{l} \right)\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times {10}^3}{{10}^{- 1}} \times {10}^{- 10} [4 \times 2 + 4 \times 3 + 3 \times 2]\]
\[ = 9 \times (8 + 12 + 6)\]
\[ = 9 \times 26 = 234 \] J
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The electrostatic force on a small sphere of charge 0.4 μC due to another small sphere of charge − 0.8 μC in air is 0.2 N.
- What is the distance between the two spheres?
- What is the force on the second sphere due to the first?
Find the dimensional formula of ε0.
Suppose the second charge in the previous problem is −1.0 × 10−6 C. Locate the position where a third charge will not experience a net force.
Estimate the number of electrons in 100 g of water. How much is the total negative charge on these electrons?
Three equal charges, 2.0 × 10−6 C each, are held at the three corners of an equilateral triangle of side 5 cm. Find the Coulomb force experienced by one of the charges due to the other two.
Two small spheres, each with a mass of 20 g, are suspended from a common point by two insulating strings of length 40 cm each. The spheres are identically charged and the separation between the balls at equilibrium is found to be 4 cm. Find the charge on each sphere.
A particle with a charge of 2.0 × 10−4 C is placed directly below and at a separation of 10 cm from the bob of a simple pendulum at rest. The mass of the bob is 100 g. What charge should the bob be given so that the string becomes loose?
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C is held fixed on a horizontal table. A second charged particle of mass 80 g stays in equilibrium on the table at a distance of 10 cm from the first charge. The coefficient of friction between the table and this second particle is μ = 0.2. Find the range within which the charge of this second particle may lie.
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. Assuming x<<d, show that this force is proportional to x.
Answer the following question.
What is relative permittivity?
Write a short note on superposition principle.
Three charges +Q, q, +Q are placed respectively, at distance, 0, d/2 and d from the origin, on the X-axis. If the net force experienced by +Q, placed at x = 0, is zero then value of q is ____________.
A force F acts between sodium and chlorine ions of salt (sodium chloride) when put 1 cm apart in air. The permittivity of air and dielectric constant of water are `epsilon_0` and K respectively. When a piece of salt is put in water, electrical force acting between sodium and chlorine ions 1 cm apart is ____________.
The electric force acting between two point charges kept at a certain distance in vacuum is 16 N. If the same two charges are kept at the same distance in a medium of dielectric constant 8, the electric force acting between them is ____________ N.
SI unit of permittivity of free space is ______.
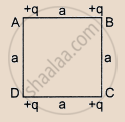
Four equal charges q are placed at the four comers A, B, C, D of a square of length a. The magnitude of the force on the charge at B will be ______.
Electric charge of any system is ______.
Two point charges Q each are placed at a distance d apart. A third point charge q is placed at a distance x from the mid-point on the perpendicular bisector. The value of x at which charge q will experience the maximum Coulomb's force is ______.
Four charges equal to −Q are placed at the four a corners of a square and charge q is at its centre. If the system is in equilibrium, the value of q is ______.
What is meant by the statement: "Relative permittivity of water is 81"?
