Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Identify the optically active compounds from the following:
(i) \[\ce{[Co(en)3]^{3+}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{[trans - [Co(en)2Cl2]^+}\]
(iii) \[\ce{cis - [Co(en)2Cl2]^+}\]
(iv) \[\ce{[Cr(NH3)5Cl]}\]
Solution
(i) \[\ce{[Co(en)3]^{3+}}\]
(iii) \[\ce{cis - [Co(en)2Cl2]^+}\]
Explanation:
\[\ce{[Co(en)3]^{3+}}\] and \[\ce{[Co(en)2Cl2]^{2+}}\] are optically active compounds because their mirror images are non-superimposable isomer.
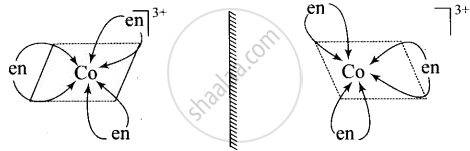
Non – superimposable isomers of \[\ce{[Co(en)3]^{3+}}\]
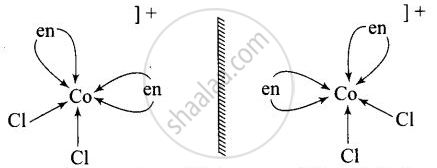
Non – superimosable isomers of \[\ce{[Co(en)2Cl2]^+}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain cationic complexes and anionic complexes of co-ordination compounds.
Draw the structure of optical isomers of [Cr(C2O4)3]3−.
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of [Co(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+.
Write the IUPAC name of [Co(en)2Cl2]+ ion and draw the structures of its geometrical isomers.
Answer the following question.
Write IUPAC name of the complex [Pt(en)2CI2]. Draw structures of geometrical isomers for this complex.
Assertion (A): Trans [CrCl2(ox)2]3− shows optical isomerism.
Reason (R): Optical isomerism is common in octahedral complexes involving didentate ligands.
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and draw the structure for isomers:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]}\]
Indicate the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure for this isomer:
[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]
Indicate the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure for this isomer: \[\ce{[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]}\]
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure for this isomer:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]}\]
