Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If \[\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = 0\] can you say that
(a) \[\vec{A} = \vec{B} ,\]
(b) \[\vec{A} \neq \vec{B}\] ?
Solution
If \[\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = 0\], then both the vectors are either parallel or antiparallel, i.e., the angle between the vectors is either \[0^\circ \text { or } 180^\circ\].
\[\vec{A} \vec{ B } \sin\ \theta \ \hat { n } = 0.......\left(\because \sin0^\circ= \sin180^\circ = 0\right)\]
Both the conditions can be satisfied:
(a) \[\vec{A} = \vec{B} ,\] i.e., the two vectors are equal in magnitude and parallel to each other
(b) \[\vec{A} ≠ \vec{B} ,\] i.e., the two vectors are unequal in magnitude and parallel or anti parallel to each other.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
“Every great physical theory starts as a heresy and ends as a dogma”. Give some examples from the history of science of the validity of this incisive remark
India has had a long and unbroken tradition of great scholarship — in mathematics, astronomy, linguistics, logic and ethics. Yet, in parallel with this, several superstitious and obscurantistic attitudes and practices flourished in our society and unfortunately continue even today — among many educated people too. How will you use your knowledge of science to develop strategies to counter these attitudes ?
“It is more important to have beauty in the equations of physics than to have them agree with experiments”. The great British physicist P. A. M. Dirac held this view. Criticize this statement. Look out for some equations and results in this book which strike you as beautiful.
What are the dimensions of volume of a cube of edge a.
A dimensionless quantity
The dimensions ML−1 T−2 may correspond to
Choose the correct statements(s):
(a) All quantities may be represented dimensionally in terms of the base quantities.
(b) A base quantity cannot be represented dimensionally in terms of the rest of the base quantities.
(c) The dimensions of a base quantity in other base quantities is always zero.
(d) The dimension of a derived quantity is never zero in any base quantity.
Find the dimensions of pressure.
Find the dimensions of the coefficient of linear expansion α and
Test if the following equation is dimensionally correct:
\[v = \frac{1}{2 \pi}\sqrt{\frac{mgl}{I}};\]
where h = height, S = surface tension, \[\rho\] = density, P = pressure, V = volume, \[\eta =\] coefficient of viscosity, v = frequency and I = moment of interia.
Let \[\vec{A} = 3 \vec{i} + 4 \vec{j}\]. Write a vector \[\vec{B}\] such that \[\vec{A} \neq \vec{B}\], but A = B.
Can you have \[\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = \vec{A} \cdot \vec{B}\] with A ≠ 0 and B ≠ 0 ? What if one of the two vectors is zero?
Let \[\vec{A} = 5 \vec{i} - 4 \vec{j} \text { and } \vec{B} = - 7 \cdot 5 \vec{i} + 6 \vec{j}\]. Do we have \[\vec{B} = k \vec{A}\] ? Can we say \[\frac{\vec{B}}{\vec{A}}\] = k ?
A situation may be described by using different sets coordinate axes having different orientation. Which the following do not depended on the orientation of the axis?
(a) the value of a scalar
(b) component of a vector
(c) a vector
(d) the magnitude of a vector.
The magnitude of the vector product of two vectors \[\left| \vec{A} \right|\] and \[\left| \vec{B} \right|\] may be
(a) greater than AB
(b) equal to AB
(c) less than AB
(d) equal to zero.
A vector \[\vec{A}\] makes an angle of 20° and \[\vec{B}\] makes an angle of 110° with the X-axis. The magnitudes of these vectors are 3 m and 4 m respectively. Find the resultant.
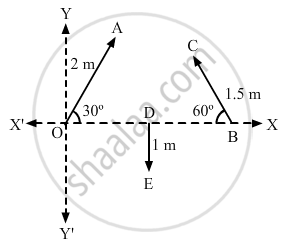
Refer to figure (2 − E1). Find (a) the magnitude, (b) x and y component and (c) the angle with the X-axis of the resultant of \[\overrightarrow{OA}, \overrightarrow{BC} \text { and } \overrightarrow{DE}\].
Let \[\vec{a} = 2 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} + 4 \vec{k} \text { and } \vec{b} = 3 \vec{i} + 4 \vec{j} + 5 \vec{k}\] Find the angle between them.
If \[\vec{A} , \vec{B} , \vec{C}\] are mutually perpendicular, show that \[\vec{C} \times \left( \vec{A} \times \vec{B} \right) = 0\] Is the converse true?
Round the following numbers to 2 significant digits.
(a) 3472, (b) 84.16. (c)2.55 and (d) 28.5
