Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If `u=sin^(-1)((x+y)/(sqrtx+sqrty))`,Prove that
`x^2u_(x x)+2xyu_(xy)+y^2u_(yy)=(-sinu.cos2u)/(4cos^3u)`
Solution
`u=sin^(-1)((x+y)/(sqrtx+sqrty))`
Put x = xt and y = yt to find degree.
`therefore u=sin^(-1)((xt+yt)/(sqrt(xt)+sqrt(yt)))`
`therefore sinu=t^(1/2)(x+y)/(sqrtx+sqrty)=t^(1/2).f(x,y)`
The function sin u is homogeneous with degree ½.
But sin u is the function of u and u is the function of x and y.
By Euler’s theorem ,
`xu_x+yu_y=G(u)=n(f(u))/(f'(u))=1/2tanu`
`therefore x^2u_(x x)+2xyu_(xy)+y^2u_(yy)=G(u)[G'(u)-1]`
`=1/2tanu[(sec^2u-2)/2]`
`=1/4tanu[[tan^2u-1)/1]`
`=1/4xx(sinu)/(cosu)[(sin^2u-cos^2u)/(cos^2u)]`
`therefore x^2u_(x x)+2xyu_(xy)+y^2u_(yy)=(-sinu.cos2u)/(4cos^3u)`
Hence Proved.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If x = u+v+w, y = uv+vw+uw, z = uvw and φ is a function of x, y and z
Prove that 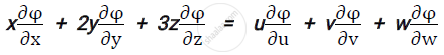
If tan(θ+iφ)=tanα+isecα
Prove that
1)`e^(2varphi)=cot(varphi/2)`
2) `2theta=npi+pi/2+alpha`
State Euler’s theorem on homogeneous function of two variables and if `u=(x+y)/(x^2+y^2)` then evaluate `x(delu)/(delx)+y(delu)/(dely`
If u =`f((y-x)/(xy),(z-x)/(xz)),` show that `x^2(delu)/(delx)+y^2(delu)/(dely)+z^2(delu)/(delz)=0`.
State and Prove Euler’s Theorem for three variables.
State and prove Euler’s Theorem for three variables.
If z = f (x, y) where x = eu +e-v, y = e-u - ev then prove that `(delz)/(delu)-(delz)/(delv)=x(delz)/(delx)-y(delz)/(dely).`
If U `=sin^(-1)[(x^(1/3)+y^(1/3))/(x^(1/2)+y^(1/2))]`prove that `x^2(del^2u)/(del^2x)+2xy(del^2u)/(delxdely)+y^2(del^2u)/(del^2y)=(tanu)/144[tan^2"U"+13].`
