Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a quadrilateral PQRS, the diagonals PR and QS intersect each other at the point T. If PT:TR = QT :TS = 1:2, show that ΔPTQ - DRTS
Solution
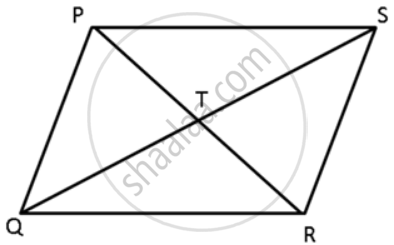
Consider ΔPTQ and ΔRTS,
`"PT"/"TR" = "QT"/"TS" = (1)/(2)` ...(Given)
∠PTQ = ∠RTS ...(Vertically Opposite angles)
⇒ ΔPTQ ∼ ΔRTS. ...(SAS criterion for Similarity)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
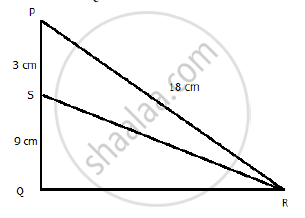
In the following figure, in Δ PQR, seg RS is the bisector of ∠PRQ.
PS = 3, SQ = 9, PR = 18. Find QR.
In the figure given below, Ray PT is bisector of ∠QPR. If PQ = 5.6 cm, QT = 4 cm and TR = 5 cm, find the value of x .
In the following figure, DE || OQ and DF || OR, show that EF || QR.

A line PQ is drawn parallel to the base BC of ∆ABC which meets sides AB and AC at points P and Q respectively. If AP = `1/3` PB; find the value of:
- `"Area of ΔABC"/"Area of ΔAPQ"`
- `"Area of ΔAPQ"/"Area of trapezium PBCQ"`
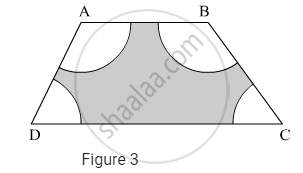
In Figure 3, ABCD is a trapezium with AB || DC, AB = 18 cm, DC = 32 cm and the distance between AB and DC is 14 cm. If arcs of equal radii 7 cm have been drawn, with centres A,B, C and D, then find the area of the shaded region.
In Δ ABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. If AD= 4cm, DB=4.Scm, AE=6.4cm and EC=7.2cm, find if DE is parallel to BC or not.
On a map drawn to a scale of 1 : 25000, a rectangular plot of land, ABCD is measured as AB= 12 cm and BC = 16cm. calculate the diagonal distance of the plot in km and the plot area in km2 .
In ΔABC, AB = 8cm, AC = 10cm and ∠B = 90°. P and Q are the points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that PQ = 3cm ad ∠PQA = 90. Find: Area of quadrilateral PBCQ: area of ΔABC.
Are triangles in figure similar? If yes, then write the test of similarity.
∆ABC ~ ∆PQR. If AM and PN are altitudes of ΔABC and ∆PQR respectively and AB2 : PQ2 = 4 : 9, then AM : PN = ______.
