Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In figure, points lying in the interior of the triangle PQR are ______, that in the exterior are ______ and that on the triangle itself are ______.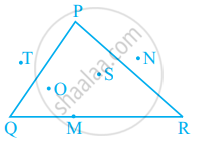
Solution
In figure, points lying in the interior of the triangle PQR are O and S, that in the exterior are T and N and that on the triangle itself are P, Q, R and M.
Explanation:
Those points which lie inside the triangle are known as interior points and those lie outside the triangle are known as exterior points.
In the given figure, points lying in the interior of ΔPQR are O and S.
Points lying in the exterior of ΔPQR are N and T.
Points lying on the ΔPQR is M, P, Q and R.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a ΔABC, if ∠A = 55°, ∠B = 40°, find ∠C.
In a ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠ACB and the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB intersect at O such that ∠BOC = 120°. Show that ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°.
Is the following statement true and false :
A triangle can have two obtuse angles.
In a Δ ABC, the internal bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at P and the external bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at Q, Prove that ∠BPC + ∠BQC = 180°.
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
If all the three angles of a triangle are equal, then each one of them is equal to
Find the unknown marked angles in the given figure:
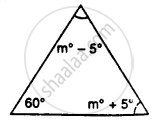
In ∆ABC, ∠A = ∠B = 62° ; find ∠C.
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4. Then the angles are
One of the angles of a triangle is 65°. If the difference of the other two angles is 45°, then the two angles are
Can we have two acute angles whose sum is a straight angle? Why or why not?
