Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
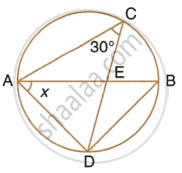
In the given circle with diameter AB, find the value of x.
Solution
∠ABD = ∠ACD = 30° ...[Angle in the same segment]
Now in ΔADB,
∠BAD + ∠ADB + ∠ABD = 180° ...[Angles of a triangle]
But, ∠ADB = 90° ...[Angle in a semi-circle]
∴ x + 90° + 30° = 180°
`=>` x + 120° = 180°
`=>` x = 180° – 120°
`=>` x = 60°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
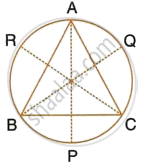
A triangle ABC is inscribed in a circle. The bisectors of angles BAC, ABC and ACB meet the circumcircle of the triangle at points P, Q and R respectively. Prove that:
- ∠ABC = 2∠APQ,
- ∠ACB = 2∠APR,
- `∠QPR = 90^circ - 1/2 ∠BAC`.
In a cyclic-trapezium, the non-parallel sides are equal and the diagonals are also equal. Prove it.
If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel; prove that:
- its other two sides are equal.
- its diagonals are equal.
In the figure, given below, CP bisects angle ACB. Show that DP bisects angle ADB.

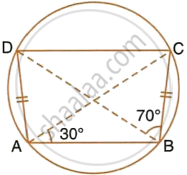
In the figure, given below, AD = BC, ∠BAC = 30° and ∠CBD = 70°.
Find:
- ∠BCD
- ∠BCA
- ∠ABC
- ∠ADB
AB is a diameter of the circle APBR, as shown in the figure. APQ and RBQ are straight lines. Find : ∠BPR
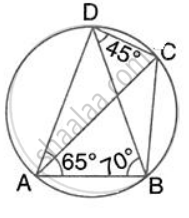
In the given figure, ∠BAD = 65°, ∠ABD = 70° and ∠BDC = 45°. Find: ∠ ACB.
Hence, show that AC is a diameter.
If I is the incentre of triangle ABC and AI when produced meets the cicrumcircle of triangle ABC in points D. f ∠BAC = 66° and ∠ABC = 80°. Calculate : ∠BIC.
In the given below the figure, AB is parallel to DC, ∠BCD = 80° and ∠BAC = 25°, Find
(i) ∠CAD, (ii) ∠CBD, (iii) ∠ADC.

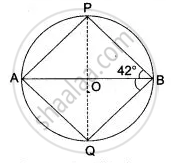
In the following figure, O is the centre of the circle, ∠ PBA = 42°.
Calculate:
(i) ∠ APB
(ii) ∠PQB
(iii) ∠ AQB