Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
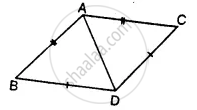
In the given figure, prove that: ∆ ABD ≅ ∆ ACD
Solution
Proof:
In Δ ABD and Δ ACD,
AD = AD ..............(common)
AB = AC ...............(given)
BD = DC ...............(given)
∴ Δ ABD ≅ Δ ACD .............(S.S.S. Axiom)
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a squared sheet, draw two triangles of equal areas such that
The triangles are congruent.
What can you say about their perimeters?
In triangles ABC and PQR, if ∠A = ∠R, ∠B = ∠P and AB = RP, then which one of the following congruence conditions applies:
In a ΔABC, if AB = AC and BC is produced to D such that ∠ACD = 100°, then ∠A =
ABC is an isosceles triangle such that AB = AC and AD is the median to base BC. Then, ∠BAD =
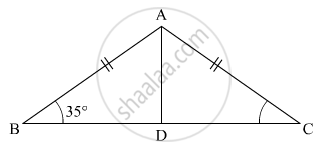
In the pair of triangles given below, the parts shown by identical marks are congruent. State the test and the one-to-one correspondence of vertices by which the triangles in the pair are congruent, the remaining congruent parts.
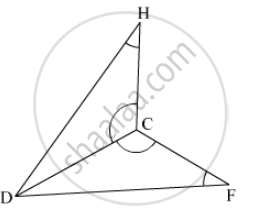
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(∠B = 90°,BC = 6cm,AB = 8cm);
ΔPQR;(∠Q = 90°,PQ = 6cm,PR = 10cm).
In the figure, AP and BQ are perpendiculars to the line segment AB and AP = BQ. Prove that O is the mid-point of the line segments AB and PQ.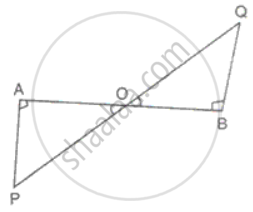
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = BC and AD = CD. Show that BD bisects both the angles ABC and ADC.
The top and bottom faces of a kaleidoscope are congruent.
Two figures are congruent, if they have the same shape.
