Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Justify that the following reaction is redox reaction; identify the species oxidized/reduced, which acts as an oxidant and which acts as a reductant.
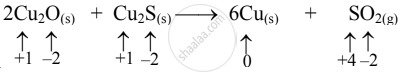
\[\ce{2Cu2O_{(S)} + Cu2S_{(S)}->6Cu_{(S)} + SO2_{(g)}}\]
Solution
\[\ce{2Cu2O_{(S)} + Cu2S_{(S)}->6Cu_{(S)} + SO2_{(g)}}\]
- Write an oxidation number of all the atoms of reactants and products.
- Identify the species that undergoes a change in oxidation number.
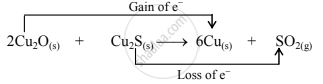
- The oxidation number of S increases from –2 to +4 and that of Cu decreases from +1 to 0. Because the oxidation number of one species increases and that of the other decreases, the reaction is a redox reaction.
- The oxidation number of S increases by loss of electrons and therefore, S is a reducing agent and it itself is oxidised. On the other hand, the oxidation number of Cu decreases by the gain of electrons, and therefore, Cu is an oxidising agent and itself is reduced.
Result:
- The given reaction is a redox reaction.
- Oxidant/oxidising agents (Reduced species): Cu2O/ Cu2S
- Reductant/reducing agent (Oxidised species): Cu2S
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{O3(g) + H2O2(l) → H2O(l) + 2O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{O3(g) + H2O2 (l) → H2O(l) + O2(g) + O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
The compound AgF2 is an unstable compound. However, if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidizing agent. Why?
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2, and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Cr2O^2-_{7(aq)} + SO^2-_{3(aq)}->Cr^3+_{ (aq)} + SO^2-_{4(aq)}(acidic)}\]
Balance the following redox equation by half-reaction method.
\[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)} + MnO^-_{4(aq)}->CO2_{(g)} + Mn^2+_{( aq)}(acidic)}\]
Balance the following redox equation by half-reaction method.
\[\ce{Bi(OH)_{3(s)} + SnO^2-_{2(aq)}->SnO^2-_{3(aq)} + Bi^_{(s)}(basic)}\]
Which of the following is INCORRECT for the following reaction?
\[\ce{2Zn_{(s)} + O2_{(g)} -> 2ZnO_{(s)}}\]
When methane is burnt completely, oxidation state of carbon changes from ______.
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{6 CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{6CO2(g) + 12H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6H2O(l) + 6O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Permanganate ion \[\ce{(MnO^{-}4)}\] reacts with sulphur dioxide gas in acidic medium to produce \[\ce{Mn^{2+}}\] and hydrogen sulphate ion.
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Fe^{2+} + H^{+} + Cr2O^{2-}7 -> Cr^{3+} + Fe^{3+} + H2O}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{MnO2 + C2O^{2-}4 -> Mn^{2+} + CO2}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{3HCl (aq) + HNO3 (aq) -> Cl2 (g) + NOCl (g) + 2H2O (l)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{HgCl2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) -> HgI2 (s) + 2KCl (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{PCl3 (l) + 3H2O (l) -> 3HCl (aq) + H3PO3 (aq)}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + SO^{2-}3 + H^{+} -> Mn^{2+} + SO^{2-}4 + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + H^{+} + Br^{-} -> Mn^{2+} + Br2 + H2O}\]
In acidic medium, reaction, \[\ce{MNO^-_4 → Mn^2+}\] an example of ____________.
The weight of CO is required to form Re2(CO)10 will be ______ g, from 2.50 g of Re2O7 according to given reaction
\[\ce{Re2O7 + CO -> Re2(CO)10 + CO2}\]
Atomic weight of Re = 186.2; C = 12 and O = 16.
In the reaction of oxalate with permanganate in an acidic medium, the number of electrons involved in producing one molecule of CO2 is ______.
Consider the following reaction:
\[\ce{xMnO^-_4 + yC2O^{2-}_4 + zH^+ -> xMn^{2+} + 2{y}CO2 + z/2H2O}\]
The values of x, y, and z in the reaction are, respectively:
\[\ce{H2O2 -> 2H^+ + O2 + 2e^-}\]; E0 = −0.68 V.
This equation represents which of the following behaviour of H2O2?
