Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Mark the incorrect statements:
(i) Catalyst provides an alternative pathway to reaction mechanism.
(ii) Catalyst raises the activation energy.
(iii) Catalyst lowers the activation energy.
(iv) Catalyst alters enthalpy change of the reaction.
Solution
(ii) Catalyst raises the activation energy.
(iv) Catalyst alters enthalpy change of the reaction.
Explanation:
(i) As the catalyst is added to the reaction medium rate of reaction increases by decreasing activation energy of molecule. Hence, it follows an alternative pathway.
(ii) Catalyst does not change the enthapy change of reaction. Energy of ‘reactant and product remain same in both catalysed and uncatalysed reaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 2 × 10−2 to 4 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea).
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for an increase of 10 K in absolute temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
In the Arrhenius equation for a first order reaction, the values of ‘A’ of ‘Ea’ are 4 x 1013 sec-1 and 98.6 kJ mol-1 respectively. At what temperature will its half life period be 10 minutes?
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1]
The rate constant of a first order reaction are 0.58 S-1 at 313 K and 0.045 S-1 at 293 K. What is the energy of activation for the reaction?
Define activation energy.
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 × 10–7 sec–1 at 50°C. What is the value of activation energy?
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
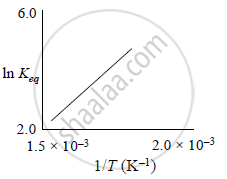
The reaction must be:
