Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the coordination compounds given in Column I with the central metal atoms given in Column II and assign the correct code:
| Column I (Coordination Compound) | Column II (Central metal atom) |
| A. Chlorophyll | 1. rhodium |
| B. Blood pigment | 2. cobalt |
| C. Wilkinson catalyst | 3. calcium |
| D. Vitamin B12 | 4. iron |
| 5. magnesium |
Options
A - (5), B - (4), C - (1), D - (2)
A - (3), B - (4), C - (5), D - (1)
A - (4), B - (3), C - (2), D - (1)
A - (3), B - (4), C - (1), D - (2)
Solution
A - (5), B - (4), C - (1), D - (2)
Explanation:
| Column I (Coordination Compound) | Column II (Central metal atom) |
| A. Chlorophyll | 5. magnesium |
| B. Blood pigment | 4. iron |
| C. Wilkinson catalyst | 1. rhodium |
| D. Vitamin B12 | 2. cobalt |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write structures of compounds A, B and C in of the following reactions
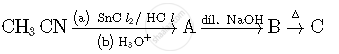
Write IUPAC name of the following Complex [Cr(NH3)3Cl3]
Write structures of compounds A and B of the following reaction :

Which of the following represents a chelate ligand?
The coordination number of the central ion may be obtained from:
In which of the following compounds the oxidation state of the nickel atom is 0?
How many ions are produced from the complex Co(NH3)6]Cl2 in solution?
Total sodium ions which are present in one formula unit of sodium ethane-1, 2-diaminetetraacetatochromate (II) and sodium hexanitrito cobaltate (III) are ______.
What is meant by the chelate effect? Give an example.
In the complex ion \[\ce{[CoCl(en)2ONO]+}\], the coordination number and the oxidation number of the central metal ion are ______ and ______.
