Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given below:
`E_("F"_2//"F"^-)^Θ` = 2.87 V, `"E"_(("Li"^(+))//("Li"^-))^Θ` = − 3.5V, `"E"_(("Au"^(3+))//("Au"))^Θ` = 1.4 V, `"E"_(("Br"_(2))//("Br"^-))^Θ` = 1.09 V
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) F2 | (a) metal is the strongest reducing agent |
| (ii) Li | (b) metal ion which is the weakest oxidising agent |
| (iii) Au3+ | (c) non metal which is the best oxidising agent |
| (iv) Br– | (d) unreactive metal |
| (v) Au | (e) anion that can be oxidised by Au3+ |
| (vi) Li+ | (f) anion which is the weakest reducing agent |
| (vii) F– | (g) metal ion which is an oxidising agent |
Solution
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) F2 | (c) non metal which is the best oxidising agent |
| (ii) Li | (a) metal is the strongest reducing agent |
| (iii) Au3+ | (g) metal ion which is an oxidising agent |
| (iv) Br– | (e) anion that can be oxidised by Au3+ |
| (v) Au | (d) unreactive metal |
| (vi) Li+ | (b) metal ion which is the weakest oxidising agent |
| (vii) F– | (f) anion which is the weakest reducing agent |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
The conductivity of sodium chloride at 298 K has been determined at different concentrations and the results are given below:
| Concentration/M | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.020 | 0.050 | 0.100 |
| 102 × κ/S m−1 | 1.237 | 11.85 | 23.15 | 55.53 | 106.74 |
Calculate `∧_"m"`for all concentrations and draw a plot between `∧_"m"`and `"c"^(1/2)`. Find the value of `∧_"m"^0`.
Write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
The S.I. unit of cell constant for conductivity cell is __________.
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
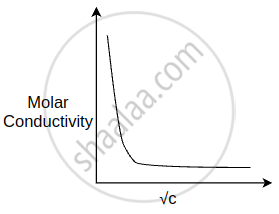
The electrolyte X is ______.
The unit of molar conductivity is ______.
