Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Name the gas evolved when zinc granules are treated/heated with:
sodium hydroxide solution
What happens when zinc granules are heated with sodium hydroxide solution? Write equation of the reaction which takes place.
Solution 1
Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide, giving sodium zincate and hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + 2NaOH(aq)→ Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
Solution 2
When zinc granules are heated with sodium hydroxide (base), sodium zincate salt is formed with the liberation of hydrogen gas.
Zn (s) + 2 NaOH(aq)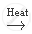 Na2 Zn O2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Na2 Zn O2 (aq) + H2 (g)
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are organic acids and mineral acids?
What happens when bases react with non-metal oxides? Explain with the help of an example. What does this reaction tell us about the nature of non-metal oxides?
Give two examples of the following:
monobasic acid
Choosing the correct words given in brackets, complete the sentence given below:
A(n) ______ (acid/basic) salt is one in which the hydrogen of an acid has been partially replaced by a ______ (metal/non-metal).
Write the balanced equation for the preparation of the following compound (as major product) starting from iron and using only one other substance:
Iron (III) chloride
The preparation of Lead sulphate from Lead carbonate is a two-step process. (Lead sulphate cannot be prepared by adding dilute Sulphuric acid to Lead carbonate.)
Why is the direct addition of dilute sulphuric acid to Lead carbonate an impractical method of preparing Lead sulphate?
What are the uses of acids?
Vinu and Priyan take their lunch at school. Vinu eats lemon rice and Priyan eats curd rice. Both lemon rice and curd rice are sour in taste. What is the reason?
What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube?
(i) Temperature of the solution decreases.
(ii) Temperature of the solution increases.
(iii) Temperature of the solution remains the same.
(iv) Salt formation takes place.
Match the chemical substances given in Column (A) with their appropriate application given in Column (B)
| Column (A) |
Column (B) |
| (A) Bleaching powder | (i) Preparation of glass |
| (B) Baking soda | (ii) Production of H2 and Cl2 |
| (C) Washing Soda | (iii) Decolourisation |
| (D) Sodium chloride | (iv) Antacid |
