Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the following picture a write down the chemical reaction with the explanation.

Solution
The rusting of iron is an oxidation process. The rust on iron does not form by a simple reaction between oxygen and iron surface. The rust is formed by an electrochemical reaction. 'Fe' oxidises to Fe2O3.XH2O (Rust) is on one part of the iron surface, while oxygen gets reduced to H2O in another part of the surface. Different regions on the surface of iron become anode and cathode.
(1) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ in the anode region.
\[\ce{Fe(s) -> Fe^{2+}(aq) + 2e^-}\]
(2) O2 is reduced to form water in the cathode region.
\[\ce{O2(g) + 4H^+(aq) + 4e^- -> 2H2O(l)}\]
When Fe2+ ions migrate from the anode region, they react with water and further get oxidised to form Fe3+ ions.
A reddish-coloured hydrated oxide is formed from Fe3+ ions. It is called rust. It collects on the surface.
\[\ce{2Fe^{3+}(aq) + 4H2O(l) -> Fe2O3.H2O(s) + 6H^+(aq)}\]
Due to various components of the atmosphere, oxidation of metals takes place, consequently resulting in their damage. This is called 'corrosion'. Iron rusts, and a reddish-coloured layer is collected on it. This is the corrosion of iron.
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is an alloy?
Tinning : Tin : : Galvanizing : _________
Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
What is anodising? Give its applications.
Write a chemical equation to show the process of corrosion of iron.
What type of chemical reaction is involved in the corrosion of iron?
In one method of rust prevention, the iron is not coated with anything. Which is this method?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The corrosion of copper produces a .............. coating of basic copper carbonate on its surface
Explain why, when a copper object remains in damp air for a considerable time, a green coating is formed on its surface. What is this process known as?
Name a common metal which is highly resistant to corrosion.
A common metal which is highly resistant to corrosion is:
(a) iron
(b) copper
(c) aluminium
(d) magnesium
Four metals P, Q, R and S are all obtained by the reduction of their oxides with carbon. Metal P is used to form a thin layer over the sheets of metal S to prevent its corrosion. Metal Q is used for electroplating tiffin boxes made of metal S whereas metal R is used in making car batteries. Metals Q and R form an alloy called solder. What are metals P, Q, R and S? How have you arrived at this conclusion?
Name the metal which is a constituent of blood pigment?
Explain with reason:
Roasting is carried out on sulphide ores and not on carbonate ores.
What are the adverse effects of corrosion?
Write three methods of preventing rusting of iron.
Give a reason why rust turns moist red litmus blue.
State whether the statement given below is true or false. If false write the correct statement.
Either oxygen or moisture is essential for rusting.
Write a short note on Alloying.
_______ is an alloy made from iron, carbon and chromium.
Bronze : _______ : : Stainless steel : Fe + Cr + C
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Match the columns.
| Group A | Group B |
| 1) Electroplating | a) Pressure cooker |
| 2) Anodising | b) Silver plated spoons |
| c) Coating of tin on copper | |
| d) Coating of Zinc on iron |
Write scientific reason.
On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time.
Write scientific reason.
Coins are made from metals and alloys.
Complete flow chart given below.

Observe the following diagram and write answers.

- Name the method.
- Explain the method.
- Give two examples of this method.
The process of coating the surface of the metal with a thin layer of zinc is called ______
Amalgam is an alloy of ____________.
The diagram shows the reaction between metal and dil. acid.
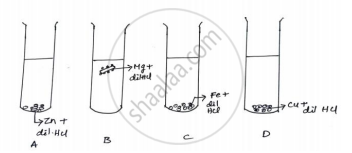
What is the reason for different behaviour of Mg in test tube B?
Galvanisation is a process used to prevent the rusting of which the following?
Give scientific reasons.
Silver amalgam is used for filling dental cavities.
In ______ process a layer of molten tin is deposited on metals.
