Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Read the bar graph given in Fig. 23.17 and answer the following questions:
(i) What information is given by the bar graph?
(ii) What was the crop-production of rice in 1970 - 71?
(iii) What is the difference between the maximum and minimum production of rice?
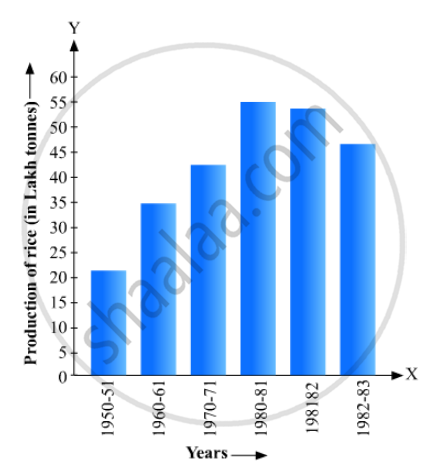
Solution
(1) The bar graph represents the production of rice crop in India in different years.
(2) According to the height of the 3rd bar from the left, the crop-production of rice in 1970-71 is 42.5 lakh tonnes.
(3) The maximum product of rice is 55 lakh tonnes (height of the 4th bar from the left) in the year 1980-81 and the minimum product of rice is 22 lakh tonnes (height of the 1st bar from the left) in the year 1950-51. Hence, the difference between maximum and minimum production of rice (in lakh tonnes) is = 55 – 22 = 33 .
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Given below are the seats won by different political parties in the polling outcome of a state assembly elections:-
| Political Party | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| Seats Won | 75 | 55 | 37 | 29 | 10 | 37 |
- Draw a bar graph to represent the polling results.
- Which political party won the maximum number of seats?
Read the bar graph given in Fig. 23.19 and answer the following questions:
(i) What information is given by the bar graph?
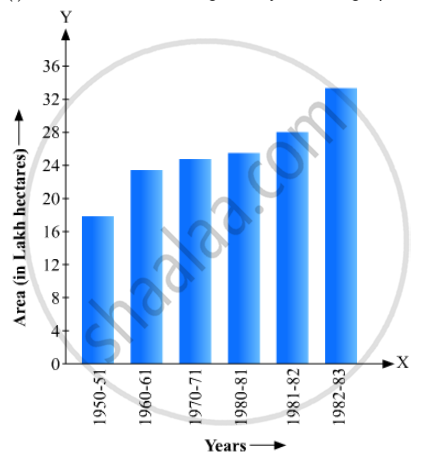
(ii) In which years the areas under the sugarcane crop were the maximum and the minimum?
(iii) State whether true or false:
The area under the sugarcane crop in the year 1982 - 83 is three times that of the year 1950 - 51
The following table gives the route length (in thousand kilometres) of the Indian Railways in some of the years:
| Year | 1960-61 | 1970-71 | 1980-81 | 1990-91 | 2000-2001 |
| Route length (in thousand km) |
56 | 60 | 61 | 74 | 98 |
Represent the above data with the help of a bar graph.
The following is the distribution of total household expenditure (in Rs.) of manual worker in a city:
| Expenditure (in Rs): |
100-150 | 150-200 | 200-250 | 250-300 | 300-350 | 350-400 | 400-450 | 450-500 |
| No. of manual workers: | 25 | 40 | 33 | 28 | 30 | 22 | 16 | 8 |
Draw a histogram and a frequency polygon representing the above data.
In a frequency distribution, ogives are graphical representation of
In the 'less than' type of ogive the cumulative frequency is plotted against
Mr. Kapoor compares the prices (in Rs.) of different items at two different shops A and B. Examine the following table carefully and represent the data by a double bar graph.
| Items | Price (in ₹) at the shop A | Price (in ₹) at the shop B |
|
Tea-set |
900 | 950 |
|
Mixie |
700 | 800 |
|
Coffee-maker |
600 | 700 |
|
Dinner set |
600 | 500 |
Harmeet earns Rs.50 000 per month. He a budget for his salary as per the following table:
| Expenses | Accommodation | Food | Clothing | Travel | Miscellaneous | saving |
| Amount (Rs.) | 12000 | 9000 | 2500 | 7500 | 4000 | 15000 |
Draw a bar graph for the above data.
Is it correct to say that in a histogram, the area of each rectangle is proportional to the class size of the corresponding class interval? If not, correct the statement.
Following table shows a frequency distribution for the speed of cars passing through at a particular spot on a high way:
| Class interval (km/h) | Frequency |
| 30 – 40 | 3 |
| 40 – 50 | 6 |
| 50 – 60 | 25 |
| 60 – 70 | 65 |
| 70 – 80 | 50 |
| 80 – 90 | 28 |
| 90 – 100 | 14 |
Draw the frequency polygon representing the above data without drawing the histogram.
