Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
Solution
Gauss' Law states that the net electric flux through any closed surface is equal to `1/epsilon_0` times the net electric charge within that closed surface.
`oint vec" E".d vec" s" = (q_(enclosed))/epsilon_o`
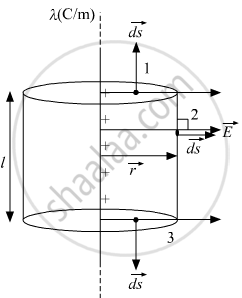
In the diagram, we have taken a cylindrical gaussian surface of radius = r and length = l.
The net charge enclosed inside the gaussian surface `q_(enclosed) = lambdal`
By symmetry, we can say that the Electric field will be in radially outward direction.
According to gauss' law,
`oint vec"E".d vec"s" = q_(enclosed)/epsilon_o`
`int_1 vec"E" .d vec"s" + int_2 vec"E" .d vec"s" + int_3 vec"E". d vec"s" = (lambdal)/epsilon_o`
`int_1 vec"E". d vec"s" & int_3 vec"E". d vec"s" "are zero", "Since" vec"E" "is perpendicular to" d vec"s"`
`int_2 vec"E" . d vec"s" = (lambdal)/epsilon_o`
`"at" 2, vec"E" and d vec"s" "are in the same direction, we can write"`
`E.2pirl = (lambdal)/epsilon_o`
`E = lambda/(2piepsilon_o r)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A charge ‘q’ is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the electric flux passing through each face of the cube?
Draw a graph of electric field E(r) with distance r from the centre of the shell for 0 ≤ r ≤ ∞.
State Gauss's law in electrostatics. Show, with the help of a suitable example along with the figure, that the outward flux due to a point charge 'q'. in vacuum within a closed surface, is independent of its size or shape and is given by `q/ε_0`
Gaussian surface cannot pass through discrete charge because ____________.
q1, q2, q3 and q4 are point charges located at points as shown in the figure and S is a spherical gaussian surface of radius R. Which of the following is true according to the Gauss' law?

The surface considered for Gauss’s law is called ______.
The Electric flux through the surface
 (i) |
 (ii) |
 (iii) |
 (iv) |
If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 over a surface, then ______.
- the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero.
- the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform.
- the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
- all charges must necessarily be outside the surface.
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
