Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Pythagoras theorem
Solution
The square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Here, the hypotenuse is the longest side and it’s always opposite the right angle
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The foot of a ladder is 6 m away from a wall and its top reaches a window 8 m above the ground. If the ladder is shifted in such a way that its foot is 8 m away from the wall, to what height does its tip reach?
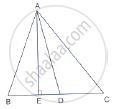
In Figure, D is the mid-point of side BC and AE ⊥ BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, ED
= x, AD = p and AE = h, prove that:
(i) `b^2 = p^2 + ax + a^2/4`
(ii) `c^2 = p^2 - ax + a^2/4`
(iii) `b^2 + c^2 = 2p^2 + a^2/2`
In a right ∆ABC right-angled at C, if D is the mid-point of BC, prove that BC2 = 4(AD2 − AC2).
ΔABC~ΔDEF such that ar(ΔABC) = 64 cm2 and ar(ΔDEF) = `169cm^2`. If BC = 4cm, find EF.
Find the length of each side of a rhombus whose diagonals are 24cm and 10cm long.
A man goes 12m due south and then 35m due west. How far is he from the starting point.
A girl walks 200m towards East and then 150m towards North. The distance of the girl from the starting point is ______.
Find the altitude of an equilateral triangle of side 8 cm.
In a ΔABC, ∠CAB is an obtuse angle. P is the circumcentre of ∆ABC. Prove that ∠CAB – ∠PBC = 90°.
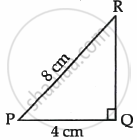
In the given figure, ΔPQR is a right triangle right angled at Q. If PQ = 4 cm and PR = 8 cm, then P is ______.