Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The area of an equilateral triangle inscribed in the circle x2 + y2 − 6x − 8y − 25 = 0 is
Options
\[\frac{225\sqrt{3}}{6}\]
25π
50π − 100
none of these
Solution
\[\frac{225\sqrt{3}}{6}\]
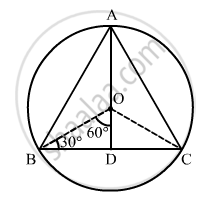
Let ABC be the required equilateral triangle.
The equation of the circle is x2 + y2 − 6x − 8y − 25 = 0.
Therefore, coordinates of the centre O is \[\left( 3, 4 \right)\].
Radius of the circle = OA = OB = OC = \[\sqrt{9 + 16 + 25} = 5\sqrt{2}\]
In \[∆\] BOD, we have:
\[\sin60° = \frac{DB}{BO}\]
\[ \Rightarrow DB = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\left( 5\sqrt{2} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow BC = 2BD = \sqrt{3}\left( 5\sqrt{2} \right) = 5\sqrt{6}\]
Now, area of \[\bigtriangleup ABC\] = \[\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}B C^2 = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \left( 5\sqrt{6} \right)^2 = \frac{\sqrt{3}\left( 150 \right)}{4} = \frac{\sqrt{3}\left( 75 \right)}{2} = \frac{\sqrt{3}\left( 225 \right)}{6}\]
square units
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the equation of the circle with:
Centre (a, b) and radius\[\sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\]
Find the equation of the circle with:
Centre (a cos α, a sin α) and radius a.
Find the centre and radius of each of the following circles:
(x − 1)2 + y2 = 4
Find the centre and radius of each of the following circles:
x2 + y2 − x + 2y − 3 = 0.
If the equations of two diameters of a circle are 2x + y = 6 and 3x + 2y = 4 and the radius is 10, find the equation of the circle.
Find the equation of a circle
which touches both the axes and passes through the point (2, 1).
Find the equation of a circle
passing through the origin, radius 17 and ordinate of the centre is −15.
Find the equation of the circle which has its centre at the point (3, 4) and touches the straight line 5x + 12y − 1 = 0.
Find the equation of the circle which touches the axes and whose centre lies on x − 2y = 3.
A circle whose centre is the point of intersection of the lines 2x − 3y + 4 = 0 and 3x + 4y− 5 = 0 passes through the origin. Find its equation.
Find the equations of the circles touching y-axis at (0, 3) and making an intercept of 8 units on the X-axis.
If the line y = \[\sqrt{3}\] x + k touches the circle x2 + y2 = 16, then find the value of k.
If the line 2x − y + 1 = 0 touches the circle at the point (2, 5) and the centre of the circle lies on the line x + y − 9 = 0. Find the equation of the circle.
Find the equation of the circle passing through the points:
(5, −8), (−2, 9) and (2, 1)
Find the equation of the circle passing through the points:
(0, 0), (−2, 1) and (−3, 2)
Show that the points (5, 5), (6, 4), (−2, 4) and (7, 1) all lie on a circle, and find its equation, centre and radius.
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the origin and cuts off chords of lengths 4 and 6 on the positive side of the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the points (2, 3) and (4,5) and the centre lies on the straight line y − 4x + 3 = 0.
Find the equation of the circle circumscribing the rectangle whose sides are x − 3y = 4, 3x + y = 22, x − 3y = 14 and 3x + y = 62.
The abscissae of the two points A and B are the roots of the equation x2 + 2ax − b2 = 0 and their ordinates are the roots of the equation x2 + 2px − q2 = 0. Find the equation of the circle with AB as diameter. Also, find its radius.
ABCD is a square whose side is a; taking AB and AD as axes, prove that the equation of the circle circumscribing the square is x2 + y2 − a (x + y) = 0.
The line 2x − y + 6 = 0 meets the circle x2 + y2 − 2y − 9 = 0 at A and B. Find the equation of the circle on AB as diameter.
Find the equations of the circles which pass through the origin and cut off equal chords of \[\sqrt{2}\] units from the lines y = x and y = − x.
If the radius of the circle x2 + y2 + ax + (1 − a) y + 5 = 0 does not exceed 5, write the number of integral values a.
Write the area of the circle passing through (−2, 6) and having its centre at (1, 2).
If the equation of a circle is λx2 + (2λ − 3) y2 − 4x + 6y − 1 = 0, then the coordinates of centre are
The radius of the circle represented by the equation 3x2 + 3y2 + λxy + 9x + (λ − 6) y + 3 = 0 is
If the point (λ, λ + 1) lies inside the region bounded by the curve \[x = \sqrt{25 - y^2}\] and y-axis, then λ belongs to the interval
The equation of a circle with radius 5 and touching both the coordinate axes is
The equation of the circle passing through the origin which cuts off intercept of length 6 and 8 from the axes is
If (−3, 2) lies on the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x2 + y2 + 6x + 8y − 5 = 0, then c =
The equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle whose sides are the lines y = x + 2, 3y = 4x, 2y = 3x is ______.
Equation of a circle which passes through (3, 6) and touches the axes is ______.
Equation of the circle with centre on the y-axis and passing through the origin and the point (2, 3) is ______.
The equation of a circle with origin as centre and passing through the vertices of an equilateral triangle whose median is of length 3a is ______.
