Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
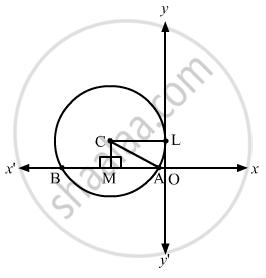
Find the equations of the circles touching y-axis at (0, 3) and making an intercept of 8 units on the X-axis.
Solution
Case I: The centre lies in first quadrant.

Let the required equation be
In \[\bigtriangleup\]CAM:
\[ \Rightarrow CA = 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow CL = CA = 5\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the equation of the circle with:
Centre (a, b) and radius\[\sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\]
Find the equation of the circle with:
Centre (0, −1) and radius 1.
Find the equation of the circle with:
Centre (a cos α, a sin α) and radius a.
Find the centre and radius of each of the following circles:
(x + 5)2 + (y + 1)2 = 9
Find the equation of the circle passing through the point of intersection of the lines x + 3y = 0 and 2x − 7y = 0 and whose centre is the point of intersection of the lines x + y + 1 = 0 and x − 2y + 4 = 0.
Find the equation of the circle whose centre lies on the positive direction of y - axis at a distance 6 from the origin and whose radius is 4.
If the equations of two diameters of a circle are 2x + y = 6 and 3x + 2y = 4 and the radius is 10, find the equation of the circle.
Find the equation of a circle which touches x-axis at a distance 5 from the origin and radius 6 units.
Find the equation of the circle which touches the axes and whose centre lies on x − 2y = 3.
A circle whose centre is the point of intersection of the lines 2x − 3y + 4 = 0 and 3x + 4y− 5 = 0 passes through the origin. Find its equation.
A circle of radius 4 units touches the coordinate axes in the first quadrant. Find the equations of its images with respect to the line mirrors x = 0 and y = 0.
Find the equations of the circles passing through two points on Y-axis at distances 3 from the origin and having radius 5.
The circle x2 + y2 − 2x − 2y + 1 = 0 is rolled along the positive direction of x-axis and makes one complete roll. Find its equation in new-position.
One diameter of the circle circumscribing the rectangle ABCD is 4y = x + 7. If the coordinates of A and B are (−3, 4) and (5, 4) respectively, find the equation of the circle.
Find the coordinates of the centre and radius of each of the following circles: 2x2 + 2y2 − 3x + 5y = 7
Find the equation of the circle which passes through (3, −2), (−2, 0) and has its centre on the line 2x − y = 3.
Show that the points (5, 5), (6, 4), (−2, 4) and (7, 1) all lie on a circle, and find its equation, centre and radius.
Find the equation of the circle which circumscribes the triangle formed by the lines
x + y = 2, 3x − 4y = 6 and x − y = 0.
Find the equation to the circle which passes through the points (1, 1) (2, 2) and whose radius is 1. Show that there are two such circles.
Find the equation of the circle concentric with x2 + y2 − 4x − 6y − 3 = 0 and which touches the y-axis.
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the points (2, 3) and (4,5) and the centre lies on the straight line y − 4x + 3 = 0.
Find the equation of the circle the end points of whose diameter are the centres of the circles x2 + y2 + 6x − 14y − 1 = 0 and x2 + y2 − 4x + 10y − 2 = 0.
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the origin and cuts off intercepts aand b respectively from x and y - axes.
Find the equation of the circle whose diameter is the line segment joining (−4, 3) and (12, −1). Find also the intercept made by it on y-axis.
Find the equation of the circle which circumscribes the triangle formed by the lines x = 0, y = 0 and lx + my = 1.
Find the equations of the circles which pass through the origin and cut off equal chords of \[\sqrt{2}\] units from the lines y = x and y = − x.
If the abscissae and ordinates of two points P and Q are roots of the equations x2 + 2ax − b2 = 0 and x2 + 2px − q2 = 0 respectively, then write the equation of the circle with PQ as diameter.
Write the equation of the unit circle concentric with x2 + y2 − 8x + 4y − 8 = 0.
If 2x2 + λxy + 2y2 + (λ − 4) x + 6y − 5 = 0 is the equation of a circle, then its radius is
The number of integral values of λ for which the equation x2 + y2 + λx + (1 − λ) y + 5 = 0 is the equation of a circle whose radius cannot exceed 5, is
If the point (2, k) lies outside the circles x2 + y2 + x − 2y − 14 = 0 and x2 + y2 = 13 then k lies in the interval
The equation of the incircle formed by the coordinate axes and the line 4x + 3y = 6 is
The equation of the circle which touches the axes of coordinates and the line \[\frac{x}{3} + \frac{y}{4} = 1\] and whose centres lie in the first quadrant is x2 + y2 − 2cx − 2cy + c2 = 0, where c is equal to
If (x, 3) and (3, 5) are the extremities of a diameter of a circle with centre at (2, y), then the values of x and y are
If (−3, 2) lies on the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x2 + y2 + 6x + 8y − 5 = 0, then c =
The equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle whose sides are the lines y = x + 2, 3y = 4x, 2y = 3x is ______.
