Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The dimensions of the model of a multistoreyed building are 1 m by 60 cm by 1.20 m. If the scale factor is 1 : 50, find the actual dimensions of the building.
Also, find:
- the floor area of a room of the building, if the floor area of the corresponding room in the model is 50 sq. cm.
- the space (volume) inside a room of the model, if the space inside the corresponding room of the building is 90 m3.
Solution
The dimensions of the building are calculated as below.
Length = 1 × 50 m = 50 m
Breadth = 0.60 × 50 m = 30 m
Height = 1.20 × 50 m = 60 m
Thus, the actual dimensions of the building are 50 m × 30 m × 60 m.
i. Floor area of the room of the building
= `50 xx (50/1)^2`
= 125000 cm2
= `(125000)/(100 xx 100)`
= 12.5 m2
ii. Volume of the model of the building
`90(1/50)^3 = 90 xx (1/50) xx (1/50) xx (1/50)`
= `90 xx ((100xx100xx100)/(50xx50xx50)) cm^3`
= 720 cm3
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
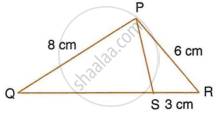
PQR is a triangle. S is a point on the side QR of ΔPQR such that ∠PSR = ∠QPR. Given QP = 8 cm, PR = 6 cm and SR = 3 cm.
- Prove ΔPQR ∼ ΔSPR.
- Find the length of QR and PS.
- `"area of ΔPQR"/"area of ΔSPR"`
Given: ABCD is a rhombus, DPR and CBR are straight lines.
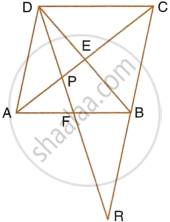
Prove that: DP × CR = DC × PR.
In ∆PQR, ∠Q = 90° and QM is perpendicular to PR. Prove that:
- PQ2 = PM × PR
- QR2 = PR × MR
- PQ2 + QR2 = PR2
In the given figure, AX : XB = 3 : 5
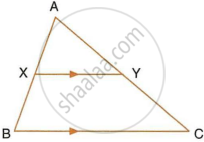
Find:
- the length of BC, if the length of XY is 18 cm.
- the ratio between the areas of trapezium XBCY and triangle ABC.
In the given triangle PQR, LM is parallel to QR and PM : MR = 3 : 4.
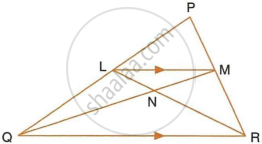
Calculate the value of ratio:
- `(PL)/(PQ)` and then `(LM)/(QR)`
- `"Area of ΔLMN"/"Area of ΔMNR"`
- `"Area of ΔLQM"/"Area of ΔLQN"`
In the figure, given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. P is a point on BC such that BP : PC = 1 : 2. DP produced meets AB produces at Q. Given the area of triangle CPQ = 20 cm2.

Calculate:
- area of triangle CDP,
- area of parallelogram ABCD.
Triangle ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC = 13 cm and BC = 10 cm. AD is
perpendicular to BC. If CE = 8 cm and EF ⊥ AB, find:
i)`"area of ADC"/"area of FEB"` ii)`"area of ΔAFEB"/"area of ΔABC"`

In a triangle PQR, L and M are two points on the base QR, such that ∠LPQ = ∠QRP and ∠RPM = ∠RQP. Prove that:
- ΔPQL ∼ ΔRPM
- QL × RM = PL × PM
- PQ2 = QR × QL
In the given figure, ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠BAC = 90°.
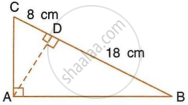
- Prove that : ΔADB ∼ ΔCDA.
- If BD = 18 cm and CD = 8 cm, find AD.
- Find the ratio of the area of ΔADB is to area of ΔCDA.
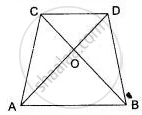
In fig. ABCD is a trapezium in which AB | | DC and AB = 2DC. Determine the ratio between the areas of ΔAOB and ΔCOD.